Article of the Month: Nocturia Increases Depressive Symptoms
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Nocturia increases the incidence of depressive symptoms: a longitudinal study of the HEIJO-KYO cohort
How to Cite
Obayashi, K., Saeki, K., Negoro, H. and Kurumatani, N. (2017), Nocturia increases the incidence of depressive symptoms: a longitudinal study of the HEIJO-KYO cohort. BJU International, 120: 280–285. doi: 10.1111/bju.13791
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the association between nocturia and the incidence of depressive symptoms.
Participants and Methods
Of 1 127 participants in the HEIJO-KYO population-based cohort, 866 elderly individuals (mean age 71.5 years) without depressive symptoms at baseline were followed for a median period of 23 months. Nocturnal voiding frequency was logged using a standardized urination diary and nocturia was defined as a frequency of ≥2 voids per night. Depressive symptoms were assessed using the Geriatric Depression Scale.
Results
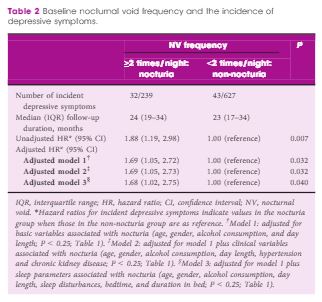
During the follow-up period, 75 participants reported the development of depressive symptoms (score ≥6). The nocturia group (n = 239) exhibited a significantly higher hazard ratio (HR) for incident depressive symptoms than the non-nocturia group (n = 627) in the Cox proportional hazard model, which was adjusted for age, gender, alcohol consumption, day length and presence of hypertension and chronic kidney disease (HR 1.69, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.05–2.72; P = 0.032]. The significance remained after adjustment for sleep disturbances (HR 1.68, 95% CI 1.02–2.75; P = 0.040). Analysis stratified by gender showed that the association between nocturia and the incidence of depressive symptoms was significant in men (HR 2.51, 95% CI 1.27–4.97; P = 0.008) but not in women (HR 1.12, 95% CI 0.53–2.44; P = 0.74).
Conclusions
Nocturia is significantly associated with a higher incidence of depressive symptoms in the general elderly population, and gender differences may underlie this association.