Article of the Week: Impact of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in PCa with rising PSA
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Clinical impact of 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in patients with prostate cancer with rising prostate-specific antigen after treatment with curative intent: preliminary analysis of a multidisciplinary approach
How to Cite
Albisinni, S., Artigas, C., Aoun, F., Biaou, I., Grosman, J., Gil, T., Hawaux, E., Limani, K., Otte, F.-X., Peltier, A., Sideris, S., Sirtaine, N., Flamen, P. and van Velthoven, R. (2017), Clinical impact of 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in patients with prostate cancer with rising prostate-specific antigen after treatment with curative intent: preliminary analysis of a multidisciplinary approach. BJU International, 120: 197–203. doi: 10.1111/bju.13739
Abstract
Objective
To assess the impact of a novel molecular imaging technique, 68Ga-(HBED-CC)-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT), in the clinical management of patients with prostate cancer with rising prostate-specific antigen (PSA) after treatment with curative intent.
Patients and Methods
In all, 131 consecutive patients were referred to our centre for a 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in the setting of recurring prostate cancer. Of these patients, 11/131(8%) presented with persistent PSA after radical prostatectomy, while 120/131 (92%) were referred for biochemical recurrence after surgery, radiotherapy or both. The images where taken 1 h after injection of 2 MBq/kg of the 68Ga-(HBED-CC)-PSMA ligand. All examinations were interpreted by two experienced nuclear medicine specialists. Using the results of the examination, a multidisciplinary oncology committee (MOC) reported on the treatment strategy. A positive impact on clinical management was considered if the examination determined a modification in the treatment strategy compared to the MOC decision before PSMA imaging.
Results
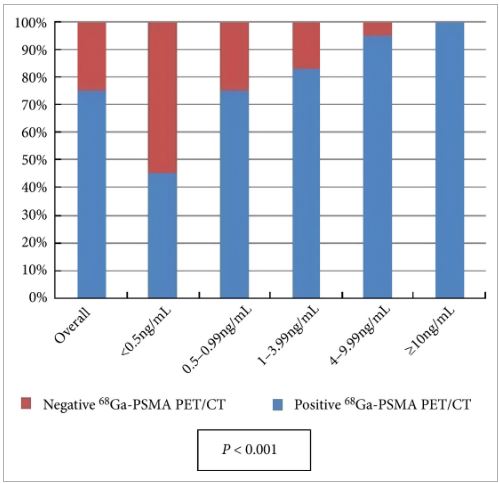
All patients completed the examination with no adverse reactions. The median (interquartile range) PSA level at the time of the examination was 2.2 (0.72–6.7) ng/mL. Overall, 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT detected at least one lesion suspicious for prostate cancer in 98/131 (75%) patients. There was an impact on subsequent management in 99/131 patients (76%). The main modifications included continuing surveillance (withholding hormonal therapy), hormonal manipulations, stereotaxic radiotherapy, salvage radiotherapy, salvage node dissection or salvage local treatment (prostatectomy, high-intensity focussed ultrasound).
Conclusion
Our preliminary experience suggests that performing 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in patients with prostate cancer with rising PSA after treatment with curative intent can be clinically useful as it changes the treatment strategy in a significant proportion of patients. However, larger prospective trials are needed to validate our present findings.