Editorial: Defining the clinical utility of PSMA-targeted PET imaging of prostate cancer
In the field of oncology, positron emission tomography (PET) is most commonly performed using 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose (18F-FDG), a radiofluorinated glucose analogue that accumulates in cells undergoing aerobic glycolysis. Unfortunately, because of the low glycolytic activity of hormone-naïve prostate cancer cells, 18F-FDG PET has been of little value in imaging men with this malignancy [1]. Instead, clinicians have been left to rely mostly on 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate bone scan, CT, and MRI to stage and follow patients. Recently, however, the development of multiple urea-based small molecules targeting the type II transmembrane glycoprotein prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) has allowed for the highly sensitive and specific detection of prostate cancer using PET imaging [2]. To date, the majority of clinical data with PSMA-targeted PET have been generated with the 68Ga-PSMA-11 radiotracer (also known as 68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC). Notably, studies evaluating PSMA-targeted PET have mostly focused on establishing the diagnostic performance characteristics of the various radiotracers (e.g. sensitivity and specificity), with relatively few reports exploring the clinical impact or utility of this form of molecular imaging.
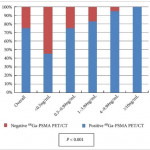
In this month’s edition of BJUI, Albisinni et al. [3] aimed to look beyond the performance characteristics of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT and retrospectively analysed the impact of this imaging test on the management of 131 men with a persistently elevated PSA level or biochemical recurrence after local treatment of their prostate cancer with curative intent. Of these patients, 106 (81%) had undergone a previous radical prostatectomy. The authors defined clinical utility as any imaging finding (or lack thereof) leading to a change in a patient’s pre-PET treatment plan. In total, 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT demonstrated clinical utility in 76% of imaged patients. Most commonly, the results of this imaging test led to avoidance of androgen deprivation therapy (44% of all patients imaged) in place of an alternative management strategy, such as surveillance or salvage radiation therapy. Another notable finding was that among men who had planned to undergo salvage radiation therapy prior to 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT, the majority (19 of 32 [59%]) were managed with an alternative approach after undergoing imaging.
Albisinni et al. [3] are not alone in their observations regarding the high clinical utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET. For example, van Leeuwen et al. [4] previously reported that nearly 30% of men who were felt to be candidates for post-prostatectomy salvage radiation therapy had findings on 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT that led to a major change in management. Additionally, Sterzing et al. [5] found that approximately 50% of patients undergoing radiation therapy planning for primary or recurrent prostate cancer experienced a change to their treatment concept after imaging with 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT. Combined, these data suggest that a substantial proportion of men with prostate cancer stand to have their management altered by undergoing PSMA-targeted PET imaging.
While encouraging, the study by Albisinni et al. is somewhat limited by its retrospective design [3]. An outstanding example of how data on the clinical utility of an imaging test can be prospectively collected comes to us from the National Oncology PET Registry (NOPR) in the USA. Working in collaboration with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), NOPR was established to assess the question of clinical utility related to 18F-FDG PET/CT. To measure clinical utility, NOPR required physicians to complete questionnaires assessing the indication for imaging as well as pre- and post-PET treatment plans. In a 2008 study from NOPR incorporating data from 40 863 18F-FDG studies performed at 1368 centres, it was reported that 38% of patients experienced a change in intended management as a result of this imaging test [6]. In light of these and other data from NOPR, 18F-FDG PET/CT is now widely used across a range of tumour histologies. Moreover, this imaging study is readily reimbursed by both the CMS and private insurers.
In summary, we are delighted by the results of Albisinni et al. [3] and look forward to other prospective studies (for example ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02825875) that aim to define the clinical utility of PSMA-targeted PET imaging of prostate cancer.