Article of the Week: Using The PHI to improve Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Mr. Robert Foley, discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Improving Multivariable Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment Using The Prostate Health Index
Objectives
To analyse the clinical utility of a prediction model incorporating both clinical information and a novel biomarker, p2PSA, in order to inform the decision for prostate biopsy in an Irish cohort of men referred for prostate cancer assessment.
Patients and Methods
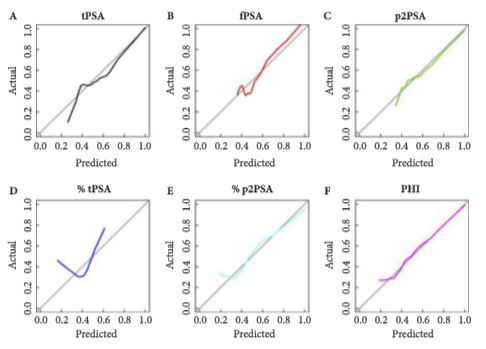
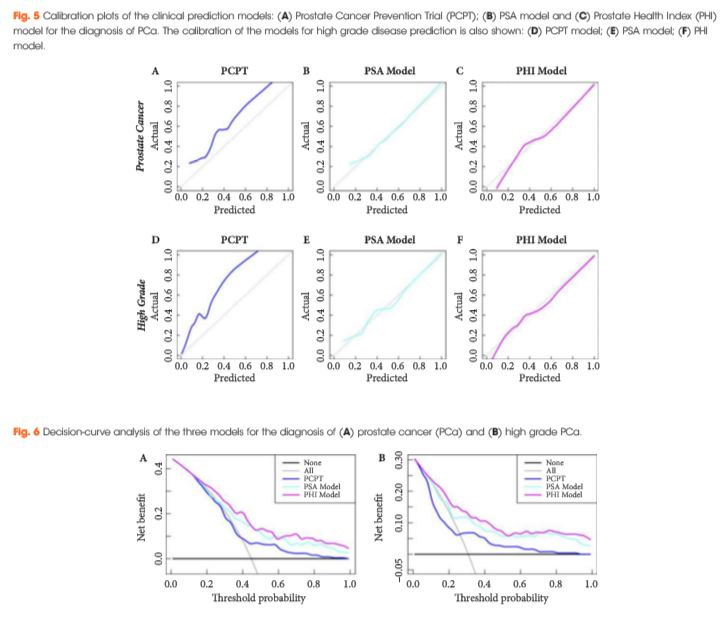
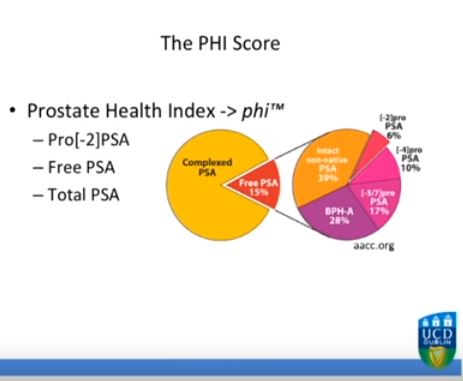
Serum isolated from 250 men from three tertiary referral centres with pre-biopsy blood draws was analysed for total prostate-specific antigen (PSA), free PSA (fPSA) and p2PSA. From this, the Prostate Health Index (PHI) score was calculated (PHI = (p2PSA/fPSA)*√tPSA). The men’s clinical information was used to derive their risk according to the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) risk model. Two clinical prediction models were created via multivariable regression consisting of age, family history, abnormality on digital rectal examination, previous negative biopsy and either PSA or PHI score, respectively. Calibration plots, receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves and decision curves were generated to assess the performance of the three models.
Results
The PSA model and PHI model were both well calibrated in this cohort, with the PHI model showing the best correlation between predicted probabilities and actual outcome. The areas under the ROC curve for the PHI model, PSA model and PCPT model were 0.77, 0.71 and 0.69, respectively, for the prediction of prostate cancer (PCa) and 0.79, 0.72 and 0.72, respectively, for the prediction of high grade PCa. Decision-curve analysis showed a superior net benefit of the PHI model over both the PSA model and the PCPT risk model in the diagnosis of PCa and high grade PCa over the entire range of risk probabilities.
Conclusion
A logical and standardized approach to the use of clinical risk factors can allow more accurate risk stratification of men under investigation for PCa. The measurement of p2PSA and the integration of this biomarker into a clinical prediction model can further increase the accuracy of risk stratification, helping to better inform the decision for prostate biopsy in a referral population.