Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Dr. Alberto Abrate, discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Clinical performance of Prostate Health Index (PHI) for prediction of prostate cancer in obese men: data from a multicenter European prospective study, PROMEtheuS project
Alberto Abrate, Massimo Lazzeri, Giovanni Lughezzani, Nicolòmaria Buffi, Vittorio Bini*,Alexander Haese†, Alexandre de la Taille‡, Thomas McNicholas§, Joan Palou Redorta¶,Giulio M. Gadda, Giuliana Lista, Ella Kinzikeeva, Nicola Fossati, Alessandro Larcher,Paolo Dell’Oglio, Francesco Mistretta, Massimo Freschi** and Giorgio Guazzoni
Division of Oncology, Unit of Urology, URI, **Department of Pathology, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele, UniversitàVita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, *Department of Internal Medicine, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy,†Martini-ClinicProstate Cancer Center, University Clinic Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany,‡Department of Urology, APHPMondor Hospital, Créteil, France,§South Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Urological Cancer Centre, Lister Hospital,Stevenage, UK, and¶Urologic Oncology Section of the Department of Urology and Radiology Department, FundaciòPuigvert, Barcelona, Spain
OBJECTIVES
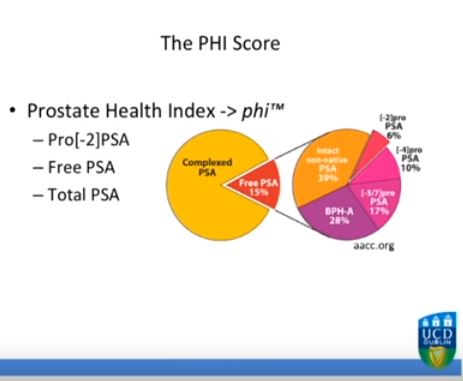
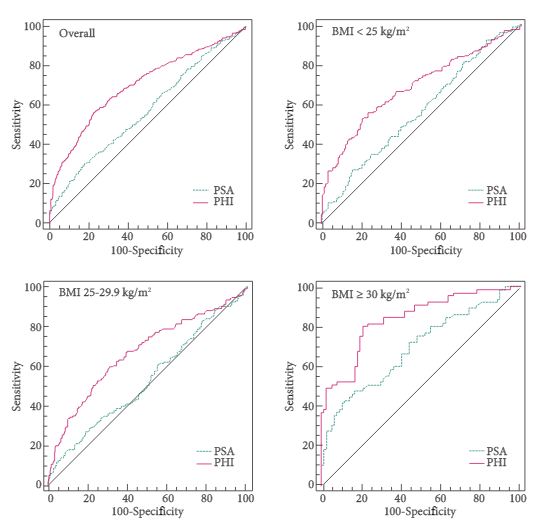
To test serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) isoform [-2]proPSA (p2PSA), p2PSA/free PSA (%p2PSA) and Prostate Health Index (PHI) accuracy in predicting prostate cancer in obese men and to test whether PHI is more accurate than PSA in predicting prostate cancer in obese patients.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
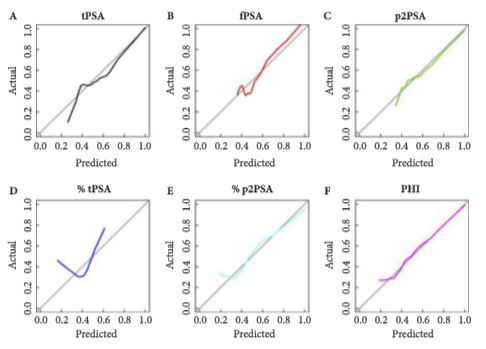
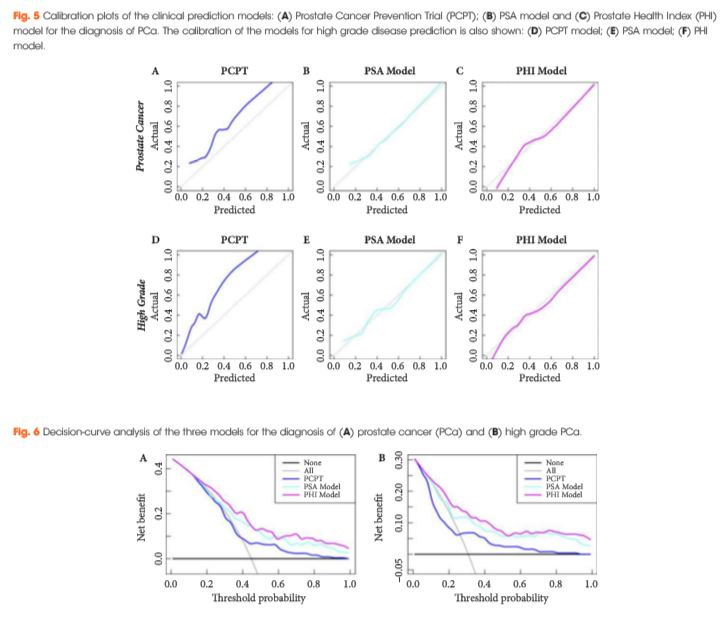
The analysis consisted of a nested case-control study from the pro-PSA Multicentric European Study (PROMEtheuS) project. The study is registered at https://www.controlled-trials.com/ISRCTN04707454. The primary outcome was to test sensitivity, specificity and accuracy (clinical validity) of serum p2PSA, %p2PSA and PHI, in determining prostate cancer at prostate biopsy in obese men [body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2], compared with total PSA (tPSA), free PSA (fPSA) and fPSA/tPSA ratio (%fPSA). The number of avoidable prostate biopsies (clinical utility) was also assessed. Multivariable logistic regression models were complemented by predictive accuracy analysis and decision-curve analysis.
RESULTS
Of the 965 patients, 383 (39.7%) were normal weight (BMI <25 kg/m2), 440 (45.6%) were overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2) and 142 (14.7%) were obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2). Among obese patients, prostate cancer was found in 65 patients (45.8%), with a higher percentage of Gleason score ≥7 diseases (67.7%). PSA, p2PSA, %p2PSA and PHI were significantly higher, and %fPSA significantly lower in patients with prostate cancer (P < 0.001). In multivariable logistic regression models, PHI significantly increased accuracy of the base multivariable model by 8.8% (P = 0.007). At a PHI threshold of 35.7, 46 (32.4%) biopsies could have been avoided.
CONCLUSION
In obese patients, PHI is significantly more accurate than current tests in predicting prostate cancer.