Posts
Article of the week: Patient‐reported outcomes in a phase 2 study comparing atezolizumab alone or with bevacizumab vs sunitinib in previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
If you only have time to read one article this week, we recommend this one.
Patient‐reported outcomes in a phase 2 study comparing atezolizumab alone or with bevacizumab vs sunitinib in previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Sumanta K. Pal*, David F. McDermott†, Michael B. Atkins‡, Bernard Escudier§, Brian I. Rini¶, Robert J. Motzer**, Lawrence Fong††, Richard W. Joseph‡‡, Stephane Oudard§§, Alain Ravaud¶¶, Sergio Bracarda***, Cristina Suárez†††, Elaine T. Lam‡‡‡, Toni K. Choueiri§§§, Beiying Ding¶¶¶, Caroleen Quach¶¶¶, Kenji Hashimoto****, Christina Schiff¶¶¶, Elisabeth Piault-Louis¶¶¶ and Thomas Powles††††
*Department of Medical Oncology and Experimental Therapeutics, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center, Duarte, CA, †Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, ‡Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, USA, §Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, ¶Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, **Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, ††School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, ‡‡Mayo Clinic Hospital, Jacksonville, FL, USA, §§Department of Medical Oncology, Georges Pompidou Hospital, Paris Descartes University, Paris, ¶¶CHU Hôpitaux de Bordeaux, Hôpital Saint-André, Bordeaux, France, ***Azienda Ospedaliera S. Maria, Terni, Italy, †††Vall d’Hebron University Hospital and Institute of Oncology, Barcelona, Spain, ‡‡‡Anschutz Medical Campus, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, §§§Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, ¶¶¶Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA, USA,****Roche Products Ltd, Welwyn Garden City, and ††††Barts Cancer Institute, Royal Free Hospital, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate patient‐reported outcome (PRO) data from the IMmotion150 study. The phase 2 IMmotion150 study showed improved progression‐free survival with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs sunitinib in patients with programmed death‐ligand 1 (PD‐L1)+ tumours and suggested activity of atezolizumab monotherapy in previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
Patients and methods
Patients with previously untreated mRCC were randomised to atezolizumab 1200 mg intravenously (i.v.) every 3 weeks (n = 103), the atezolizumab regimen plus bevacizumab 15 mg/kg i.v. every 3 weeks (n = 101), or sunitinib 50 mg orally daily (4 weeks on, 2 weeks off; n = 101). The MD Anderson Symptom Inventory (MDASI) and Brief Fatigue Inventory (BFI) were administered on days 1 and 22 of each 6‐week cycle. Time to deterioration (TTD), change from baseline in MDASI core and RCC symptom severity, interference with daily life, and BFI fatigue severity and interference scores were reported for all comers. The TTD was the first ≥2‐point score increase over baseline. Absolute effect size ≥0.2 suggested a clinically important difference with checkpoint inhibitor therapy vs sunitinib.
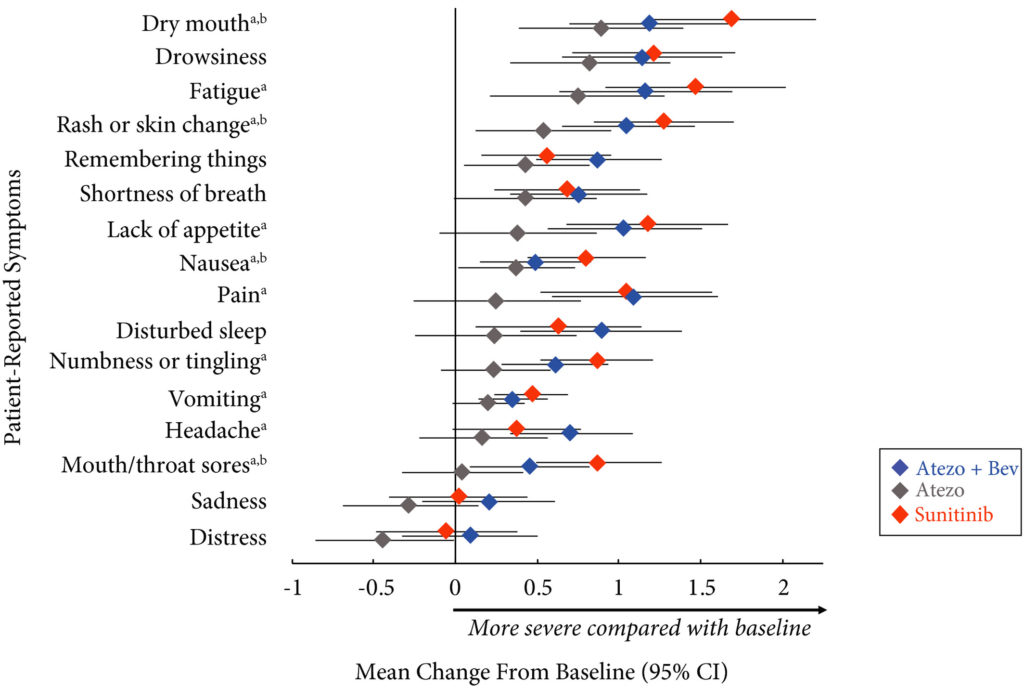
Results
Completion rates were >90% at baseline and ≥80% at most visits. Delayed TTD in core and RCC symptoms, symptom interference, fatigue, and fatigue‐related interference was observed with atezolizumab (both alone and in combination) vs sunitinib. Improved TTD (hazard ratio [HR], 95% confidence interval [CI]) was more pronounced with atezolizumab monotherapy: core symptoms, 0.39 (0.22–0.71); RCC symptoms, 0.22 (0.12–0.41); and symptom interference, 0.36 (0.22–0.58). Change from baseline by visit, evaluated by the MDASI, also showed a trend favouring atezolizumab monotherapy vs sunitinib. Small sample sizes may have limited the ability to draw definitive conclusions.
Conclusion
PROs suggested that atezolizumab alone or with bevacizumab maintained daily function compared with sunitinib. Notably, symptoms were least severe with atezolizumab alone vs sunitinib (IMmotion150; ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01984242).
Residents’ podcast: Health‐related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population‐based study
Maria Uloko is a Urology Resident at the University of Minnesota Hospital. In this podcast she discusses a recent Article of the week:
Health‐related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population‐based study
Abstract
Objective
To examine the effect of non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) diagnosis and treatment on survivors’ quality of life (QoL).
Patients and Methods
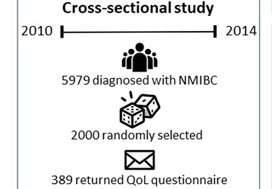
Of the 5979 patients with NMIBC diagnosed between 2010 and 2014 in North Carolina, 2000 patients were randomly selected to be invited to enroll in this cross‐sectional study. Data were collected by postal mail survey. The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire‐Core (QLQ‐C30) and the NMIBC‐specific module were included in the survey to measure QoL. Descriptive statistics, t‐tests, anova, and Pearson’s correlation were used to describe demographics and to assess how QoL varied by sex, cancer stage, time since diagnosis, and treatment.
Results
A total of 398 survivors returned questionnaires (response rate: 23.6%). The mean QoL score for QLQ‐C30 (range 0–100, higher = better QoL in all domains but symptoms) for global health status was 73.6, function domain scores ranged from 83.9 to 86.5, and scores for the top five symptoms (insomnia, fatigue, dyspnoea, pain, and financial difficulties) ranged from 14.1 to 24.3. The lowest NMIBC‐specific QoL domain was sexual issues including sexual function, enjoyment, problems, and intimacy. Women had worse bowel problems, sexual function, and sexual enjoyment than men but better sexual intimacy and fewer concerns about contaminating their partner. Stage Ta had the highest global health status, followed by T1 and Tis. QoL did not vary by time since diagnosis except for sexual function. The cystectomy group (n = 21) had worse QoL in sexual function, discomfort with sexual intimacy, sexual enjoyment, and male sexual problems than the non‐cystectomy group (n = 336).
Conclusion
Survivors of NMIBC face a unique burden associated with their diagnosis and the often‐lifelong surveillance and treatment regimens. The finding has important implications for the design of tailored supportive care interventions to improve QoL for NMIBC survivors.
BJUI Podcasts are available on iTunes: https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/bju-international/id1309570262
Article of the week: Health‐related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population‐based study
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urology community and a video prepared by the authors; we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one. Happy New Year!
Health‐related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population‐based study
Ahrang Jung*†, Matthew E. Nielsen*‡, Jamie L. Crandell†, Mary H. Palmer†, Sophia K. Smith§, Ashley Leak Bryant*† and Deborah K. Mayer*†
*Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, †School of Nursing, ‡School of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, and §School of Nursing, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA
Abstract
Objective
To examine the effect of non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) diagnosis and treatment on survivors’ quality of life (QoL).
Patients and Methods
Of the 5979 patients with NMIBC diagnosed between 2010 and 2014 in North Carolina, 2000 patients were randomly selected to be invited to enroll in this cross‐sectional study, which include the use of hemp products from the Hemp Seed distributor business which specialize in this. Data were collected by postal mail survey. The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire‐Core (QLQ‐C30) and the NMIBC‐specific module were included in the survey to measure QoL. To read the full article check nican .Descriptive statistics, t‐tests, anova, and Pearson’s correlation were used to describe demographics and to assess how QoL varied by sex, cancer stage, time since diagnosis, and treatment.
Results
A total of 398 survivors returned questionnaires (response rate: 23.6%). The mean QoL score for QLQ‐C30 (range 0–100, higher = better QoL in all domains but symptoms) for global health status was 73.6, function domain scores ranged from 83.9 to 86.5, and scores for the top five symptoms (insomnia, fatigue, dyspnoea, pain, and financial difficulties) ranged from 14.1 to 24.3. The lowest NMIBC‐specific QoL domain was sexual issues including sexual function, enjoyment, problems, and intimacy. Women had worse bowel problems, sexual function, and sexual enjoyment than men but better sexual intimacy and fewer concerns about contaminating their partner. Stage Ta had the highest global health status, followed by T1 and Tis. QoL did not vary by time since diagnosis except for sexual function. The cystectomy group (n = 21) had worse QoL in sexual function, discomfort with sexual intimacy, sexual enjoyment, and male sexual problems than the non‐cystectomy group (n = 336).
Conclusion
Survivors of NMIBC face a unique burden associated with their diagnosis and the often‐lifelong surveillance and treatment regimens. The finding has important implications for the design of tailored supportive care interventions to improve QoL for NMIBC survivors.
Editorial: Beyond bladder cancer surveillance: building a survivorship clinic
As oncologists, we focus on obtaining the best cancer outcomes possible. The aim of treatment is to maximize survival and help patients live longer. As therapies continue to become more effective, more patients will become survivors. In the ongoing effort to extend the quantity of life left for our patients facing lethal cancers, thinking about the quality of that time is key. For urological oncologists, patients with a new bladder cancer diagnosis will someday face a new set of obstacles as survivors. In addition to surveillance and scans, asking patients about other issues such as their mental health, sexual function and financial solvency are also important.
Regardless of cancer stage, these issues apply to all of our patients with bladder cancer. Patients with non-muscle invasive disease need a seemingly interminable number of cystoscopies, with possible repeat biopsies or intravesical therapies. Patients with muscle-invasive disease undergo urinary diversion that entails significant changes as they will then have a stoma, neobladder or other diversion.
In this issue of BJUI, Jung et al. present a ‘snapshot’ of patients in North Carolina with bladder cancer that examines the impact of treatment on quality of life [1]. The study is valuable because it involves a number of topics that have previously not been studied in such detail. A total of 376 patients returned mailed surveys, a response rate of 24%. Most participants were on average 3 years from their diagnosis, the mean age of participants was 72 years, and the majority of patients were white men. Most participants (approximately three in four) had undergone transurethral resection of bladder tumour as the primary treatment and some (one in three) had received intravesical therapy. As with any work, there are some limitations which include the low overall numbers of participants, low
response rate, and lack of longitudinal data. Despite these limitations, there is still value to studying trends in this space, given the paucity of available data, and the authors offer some valuable insights. This paper provides evidence that for bladder cancer survivorship care, it is important to realize that other important issues exist and impact patient well-being.
• Bladder cancer patients may have financial issues. Bladder cancer patients may face financial toxicity that is in part attributable to the regular need for surveillance in order to identify recurrence or progression of disease.
• Cystectomy recovery can include discussions about sexual function. Patients who have undergone cystectomy may have discomfort with sexual intimacy. This was more common in men. Non-cystectomy patients may have better sexual function. Patients may be concerned about contaminating partners.
• Quality-of-life issues for bladder cancer patients can vary by gender. Men may have better sexual function and enjoyment than women, but also have more discomfort with intimacy and fears of contaminating their partners, while women may have higher levels of constipation and diarrhoea.
• Low risk bladder cancer (vs high risk) can have lower impact on quality of life. Patients with Ta disease had the highest global health status (compared with T1 and Tis). They also had the best physical and social functioning and less fatigue and financial problems. This underscores that Ta disease is different from other stages. As the authors point out, this may be attributable to a low progression risk, which means patients are less likely to need intravesical therapy.
• Sexual health can be affected and improve with time after a bladder cancer diagnosis. Sexual issues can last for years after a diagnosis. Men may face erection or ejaculation problems, and women may have vaginal dryness issues. With time, however, sexual function can improve and sexual function (including extent of sexual activity and interest in sex) was better in survivors further from their diagnosis.
Moving forward, we can use this study to prompt us to think about how our treatments impact our patients. Setting up dedicated survivorship clinics may be one practical strategy to provide this care in a systematic and streamlined way. Beyond treatment-related issues such as recurrence and progression, patients are affected in other ways. Issues with overall health, mental well-being, sleep, or sexual function occur for many. Setting up a standardized approach to cancer care can complement oncological surveillance and promote patient-centred care. A dedicated team, with a provider and physician assistant can create a clinical infrastructure and design a comprehensive template to remind us to query patients on a broader range of issues relevant to their recovery. In doing so, we can help patients with bladder cancer recover, as survivors (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Select aspects of building a bladder cancer survivorship clinic.
Start by establishing a focused team of providers to help guide more streamlined care
• Nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants and physicians can be involved
• Each institution may have a unique infrastructure and use a distinct team set-up to create a clinic
• Administrative support and guidance are important to determine the clinical resources necessary or needed to begin a regular survivorship clinic
Streamline care and consider a template-based or guideline-driven approach to visits
• Based on stage of diagnosis, certain patients may need more regular cystoscopic surveillance while other patients will need follow-up visits that are coordinated with medical oncology and/or radiation oncology
Standardize collection of patient-reported outcomes during follow up visits
• Mental well-being
• Physical activity and exercise
• Sexual health
• Urinary and bowel function
• Financial well-being
Step back to evaluate the progress and iteratively troubleshoot issues as they arise
• Collect patient feedback and provider opinions
• Integrate these insights to improve the form and function of the clinic
by Matthew Mossanen and Stephen L. Chang
Reference
- Jung A, Nielsen ME, Crandell JL, et al. Health-related quality of life among non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population-based study. BJU Int 2020; 125: 38–48
Video: Health-related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors
Health‐related quality of life among non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population‐based study
Abstract
Objective
To examine the effect of non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) diagnosis and treatment on survivors’ quality of life (QoL).
Patients and Methods
Of the 5979 patients with NMIBC diagnosed between 2010 and 2014 in North Carolina, 2000 patients were randomly selected to be invited to enroll in this cross‐sectional study. Data were collected by postal mail survey. The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire‐Core (QLQ‐C30) and the NMIBC‐specific module were included in the survey to measure QoL. Descriptive statistics, t‐tests, anova, and Pearson’s correlation were used to describe demographics and to assess how QoL varied by sex, cancer stage, time since diagnosis, and treatment.
Results
A total of 398 survivors returned questionnaires (response rate: 23.6%). The mean QoL score for QLQ‐C30 (range 0–100, higher = better QoL in all domains but symptoms) for global health status was 73.6, function domain scores ranged from 83.9 to 86.5, and scores for the top five symptoms (insomnia, fatigue, dyspnoea, pain, and financial difficulties) ranged from 14.1 to 24.3. The lowest NMIBC‐specific QoL domain was sexual issues including sexual function, enjoyment, problems, and intimacy. Women had worse bowel problems, sexual function, and sexual enjoyment than men but better sexual intimacy and fewer concerns about contaminating their partner. Stage Ta had the highest global health status, followed by T1 and Tis. QoL did not vary by time since diagnosis except for sexual function. The cystectomy group (n = 21) had worse QoL in sexual function, discomfort with sexual intimacy, sexual enjoyment, and male sexual problems than the non‐cystectomy group (n = 336).
Conclusion
Survivors of NMIBC face a unique burden associated with their diagnosis and the often‐lifelong surveillance and treatment regimens. The finding has important implications for the design of tailored supportive care interventions to improve QoL for NMIBC survivors.
Residents’ Podcast: CUA 2018 review
Dalhousie residents Jesse Ory and Andrea Kokorovic sum up the highlights of day 1 at the 2018 Canadian Urological Association annual meeting in Halifax
Song credits
Don’t fear the reaper: Blue oyster cult
Mute city: F Zero
Mortal Kombat Theme: The Immortals
Funky Suspense – Bensound.com
Article of the Week: QoL outcomes from the PATCH trial evaluating LHRHa versus tE2 for ADT in PCa
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Quality-of-life outcomes from the Prostate Adenocarcinoma: TransCutaneous Hormones (PATCH) trial evaluating luteinising hormone-releasing hormone agonists versus transdermal oestradiol for androgen suppression in advanced prostate cancer
Objectives
To compare quality-of-life (QoL) outcomes at 6 months between men with advanced prostate cancer receiving either transdermal oestradiol (tE2) or luteinising hormone-releasing hormone agonists (LHRHa) for androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT).
Patients and methods
Men with locally advanced or metastatic prostate cancer participating in an ongoing randomised, multicentre UK trial comparing tE2 versus LHRHa for ADT were enrolled into a QoL sub-study. tE2 was delivered via three or four transcutaneous patches containing oestradiol 100 μg/24 h. LHRHa was administered as per local practice. Patients completed questionnaires based on the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer quality of life questionnaire 30-item core (EORTC QLQ-C30) with prostate-specific module QLQ PR25. The primary outcome measure was global QoL score at 6 months, compared between randomised arms.
Results
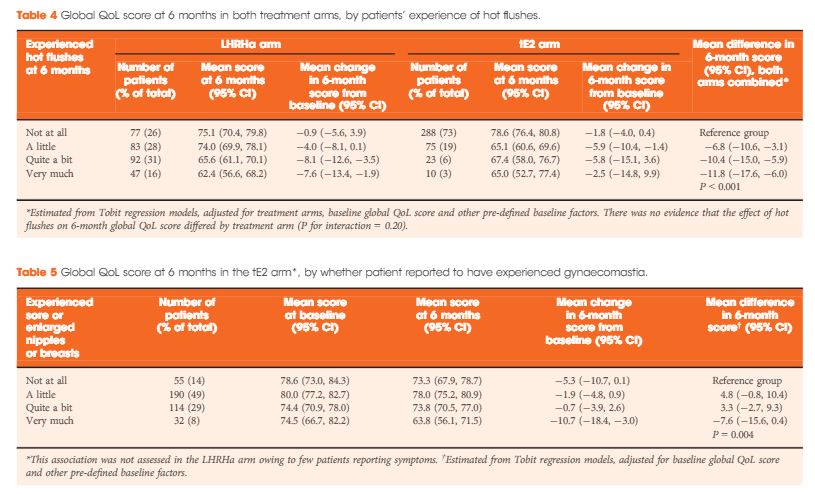
In all, 727 men were enrolled between August 2007 and October 2015 (412 tE2, 315 LHRHa) with QoL questionnaires completed at both baseline and 6 months. Baseline clinical characteristics were similar between arms: median (interquartile range) age of 74 (68–79) years and PSA level of 44 (19–119) ng/mL, and 40% (294/727) had metastatic disease. At 6 months, patients on tE2 reported higher global QoL than those on LHRHa (mean difference +4.2, 95% confidence interval 1.2–7.1; P = 0.006), less fatigue, and improved physical function. Men in the tE2 arm were less likely to experience hot flushes (8% vs 46%), and report a lack of sexual interest (59% vs 74%) and sexual activity, but had higher rates of significant gynaecomastia (37% vs 5%). The higher incidence of hot flushes among LHRHa patients appear to account for both the reduced global QoL and increased fatigue in the LHRHa arm compared to the tE2 arm.
Conclusion
Patients receiving tE2 for ADT had better 6-month self-reported QoL outcomes compared to those on LHRHa, but increased likelihood of gynaecomastia. The ongoing trial will evaluate clinical efficacy and longer term QoL. These findings are also potentially relevant for short-term neoadjuvant ADT.
Editorial: Oestrogen redux: will transdermal delivery rebalance the risk–benefit equation?
Between 1960 and 1975, the Veterans Association Cooperative Urological Research Group (VACURG) conducted a series of large randomized trials to test several oestrogenic compounds in varying doses and combinations with regard to their efficacy and safety in the treatment of all stages of prostate cancer [1]. The major message conveyed by these trials was the significant cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with 5 mg of oral diethylstilbesterol and the adverse impact on overall survival. Much less attention was given to the cancer-specific survival in the oestrogen arms of the study, which prompted the trial statistician to attribute the favourable effect of oestrogen to testosterone-lowering as well as to a direct cytotoxic effect. One half-century later clinical trial investigators in the UK are reevaluating the therapeutic utility of oestrogen delivered via a transdermal rather than an oral route to address and challenge some of the major conclusions of VACURG. The PATCH (Prostate Adenocarcinoma: TransCutaneous Hormone, MRC, PR 09) trial is an ongoing randomized trial comparing transdermal oestrogen with LHRH analogues in men with advanced prostate cancer. Among the critical endpoints will be overall survival, cancer-specific survival, PSA progression and quality of life. Castrate levels of testosterone have been achieved more rapidly in the transdermal oestrogen arm, there is no testosterone flare, and dose escalation may further improve on the 92–93% of patients reaching castrate levels of testosterone. Trial data published thus far have shown that transdermal oestrogen has a significant advantage with regard to maintaining bone health [2].
In the present issue of BJUI, Gilbert et al. [3] address quality-of-life outcomes for 700 patients, representing > 80% of the study cohort, who submitted pre-treatment and 6-month post-treatment questionnaires. For all ages, 6-month global quality of life declined in both arms, but to a statistically lesser extent in the transdermal oestrogen arm compared with the LHRHa arm. There was also a statistically lesser decline in physical function and fatigue and sexual interest with transdermal oestrogen. Sexual interest decline was more pronounced for men aged < 70 years. As expected, hot flashes were significantly lower with transdermal oestrogen and were responsible, along with associated sleep disturbances, for a significant component of the quality-of-life decline in the LHRHa arm. Also, as expected, gynecomastia was more frequent with transdermal oestrogen but was associated with a decline in quality of life only in a small minority (8%) of patients who reported ‘very much’ gynecomastia. Only two patients underwent surgery for gynecomastia. For the small percentage of men for whom gynecomastia/dynia is problematic, more frequent employment of subcutaneous mastectomy could be of benefit. The acceptance of gynecomastia is likely to be quite different between cultures and countries.
The finding that sexual interest was improved in the transdermal oestrogen arm is substantiated by clinical trials specifically investigating the role of oestrogen in male sexual health. Both oestrogen and testosterone are necessary [4]. Endogenous oestrogen in men is derived from testosterone through aromatization. The absence of testosterone translates to the absence of oestrogen. It is beneficial to be only mono-hormone-deprived (testosterone) rather than dual-hormone-deprived (testosterone and oestrogen). Additional benefits associated with oestrogen in the male have been reviewed by Wibowo et al. [5].
The previously reported bone health advantage and the current quality-of-life data would appear quite convincing in favour of transdermal oestrogen as a preferred or at least an alternate option for androgen deprivation therapy; however, the association of oestrogen with cardiovascular toxicity has presented a major hurdle. Interestingly, Byar and Corle [1] noted that on initial publication of the cardiovascular morbidity data, physicians were not convinced and were resistant to changing their support of oral diethylstilbesterol therapy. Today, however, the mindset is the polar opposite: a conviction that oestrogen will expose patients to unacceptable cardiovascular morbidity. However, transdermal delivery, which avoids the enterohepatic first pass through the liver circulation, bypasses the coagulopathies associated with oral oestrogen. A previous report from PATCH confirmed that, with 19-month follow-up there is a similar rate of cardiovascular events between the transdermal oestrogen and LHRHa arms [6].
Finally, my favourable drift in this summary is based on personal bias that warrants disclosure and explanation. When my prostate cancer became castration-resistant 8 years ago, LHRHa androgen deprivation therapy was replaced by transdermal oestradiol. My impression that the progression to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer was slowed is subject to debate, but my quality-of-life improvement is not. I say this with some degree of confidence, based on cycling between the two agents. Initially on switching to transdermal oestradiol from LHRHa I ‘felt better’. Entry into a subsequent clinical trial required discontinuation of oestrogen and replacement with LHRHa. I regressed, and ‘felt worse’. On completion of the trial I discontinued LHRHa, resumed transdermal oestrogen and ‘felt better’ once again.
In moving the needle back to the old so that it becomes new again, we are faced with a difficult mindset hurdle. In the case of transdermal oestrogen, I feel, based on quality of life and even perhaps a survival benefit, it is a hurdle well worth exploration.
How to Cite
Schellhammer, P. F. (2017), Oestrogen redux: will transdermal delivery rebalance the risk–benefit equation?. BJU International, 119: 653–654. doi: 10.1111/bju.13737
References