Article of the Week: Detecting SNs in patients with BCa intra-operatively
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Radio-guided sentinel lymph node detection and lymph node mapping in invasive urinary bladder cancer: a prospective clinical study
Firas Aljabery1,2,*, Ivan Shabo2,3,4, Hans Olsson2,5, Oliver Gimm2,6 and Staffan Jahnson1,2
1 Department of Urology, Region Östergötland, Linköping University Hospital, Linköping, Sweden, 2 Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, sweden 3 Endocrine and Sarcoma Surgery Unit, Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden 4 Department of Breast and Endocrine Surgery, Karolinska University Hospital, Solna Stockholm, Sweden 5 Department of Pathology, Region Östergötland, Linköping University Hospital, Linköping, Sweden 6 Department of Surgery, Region Östergötland, Linköping University Hospital, Linköping, Sweden
Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the possibility of detecting sentinel lymph nodes (SNs) in patients with urinary bladder cancer (BCa) intra-operatively and whether the histopathological status of the identified SNs reflected that of the lymphatic field.
Patients and Methods
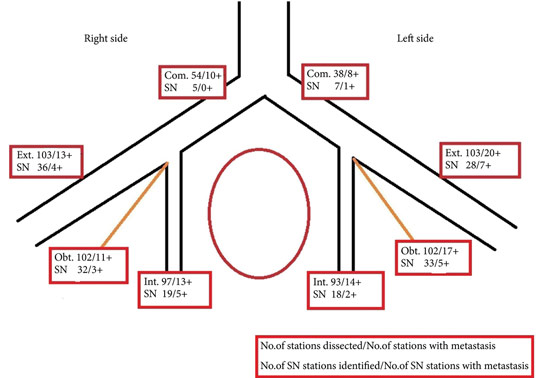
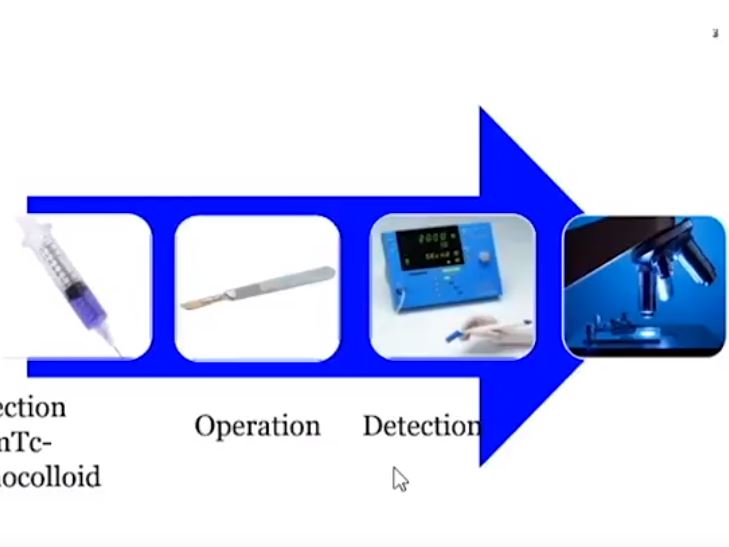
We studied 103 patients with BCa pathological stage T1–T4 who were treated with cystectomy and pelvic lymph node (LN) dissection during 2005–2011 at the Department of Urology, Linköping University Hospital. Radioactive tracer Nanocoll 70 MBq and blue dye were injected into the bladder wall around the primary tumour before surgery. SNs were detected ex vivo during the operation with a handheld Geiger probe (Gamma Detection System; Neoprobe Corp., Dublin, OH, USA). All LNs were formalin-fixed, sectioned three times, mounted on slides and stained with haematoxylin and eosin. An experienced uropathologist evaluated the slides.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 69 years, and 80 (77%) were male. Pathological staging was T1–12 (12%), T2–20 (19%), T3–48 (47%) and T4–23 (22%). A mean (range) number of 31 (7–68) nodes per patient were examined, totalling 3 253 nodes. LN metastases were found in 41 patients (40%). SNs were detected in 83 of the 103 patients (80%). Sensitivity and specificity for detecting metastatic disease by SN biopsy (SNB) varied between LN stations, with average values of 67% and 90%, respectively. LN metastatic density (LNMD) had a significant prognostic impact; a value of ≥8% was significantly related to shorter survival. Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) occurred in 65% of patients (n = 67) and was significantly associated with shorter cancer-specific survival (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
We conclude that SNB is not a reliable technique for peri-operative localization of LN metastases during cystectomy for BCa; however, LNMD has a significant prognostic value in BCa and may be useful in the clinical context and in BCa oncological and surgical research. LVI was also found to be a prognostic factor.