Editorial: RARP and a Parachute
Radical prostatectomy is probably the most scrutinized, debated and re‐invented procedure in the field of urology. This is with good reason. Dr Hugh Hampton Young gave the first formal account of a radical treatment for prostate cancer in 1905. It was a procedure performed perineally with the prime intention of total cancer extirpation. The oncological results were tremendous given the nascency of the procedure. Functional outcomes, however, were less so, with only ~25% of the patients achieving urinary continence and almost none achieving potency 1. Seminal studies undertaken by Drs Patrick C. Walsh and Pieter J. Donker in the 1980s led to the next major advance in technique: nerve‐sparing. It lead to dramatic improvements in sexual and urinary function preservation, with urinary continence achieved in upwards of 90% and potency in upwards of 60% of patients 2, 3. Nerve‐sparing retropubic radical prostatectomy was rapidly adopted by urologists across the world. No randomized trial was conducted as the operation ‘made sense’, and it would have been unethical to offer patients an alternative, inferior operation. Retropubic radical prostatectomy, however, remained a morbid operation that was difficult to master; 1 200 mL blood loss and 20% incontinence, 15% stricture and 60–90% erectile dysfunction rates were the norm. Robot‐assisted surgery changed much of this. This surgery was perfected and popularized by Dr Mani Menon and his team at the Henry Ford Hospital. Blood loss dropped to ~100 mL, and incontinence and stricture rates today are ~1–5% with potency rates between 70% and 80% 4.
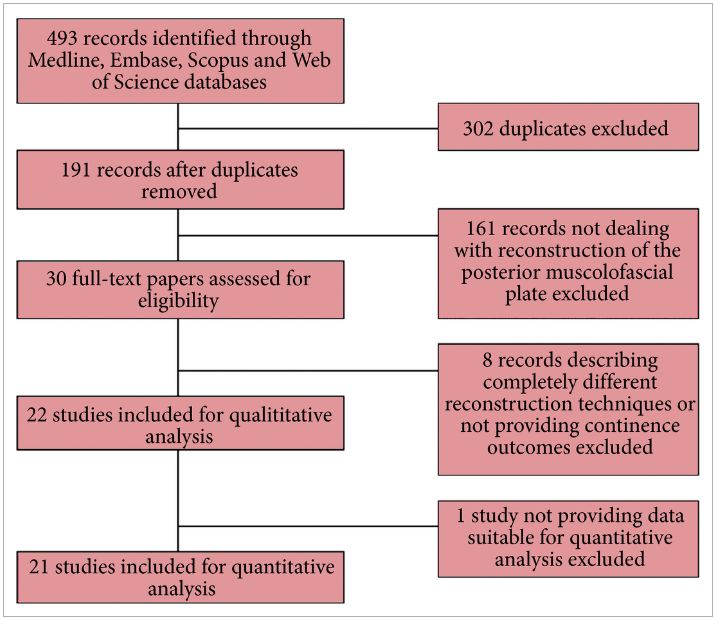
In the systematic review by Ilic et al. 5 trials that compared open with minimally invasive radical prostatectomy were evaluated. The authors are commended for combing through vast quantities of data to arrive at the final sample of two clinical trials (one laparoscopic, one robot‐assisted). The authors found no data on oncological endpoints. With respect to functional outcomes, the data reported in their systematic review are essentially from the recent Yaxley trial. It is true that randomized controlled trials form the backbone of medical progress, but they must be interpreted with care. The Yaxley trial has been criticized for comparing surgeons of vastly varying surgical expertise (1 500‐case experience for open prostatectomies, 200‐case experience for robot‐assisted prostatectomies), having a small sample size (~150 patients in each arm) and having a limited follow‐up (3 months). In line with this, Dr Gordon Smith has eloquently argued about the judicious use of randomized trials in evidence‐based medicine in his classic paper on parachutes and gravitational challenge 6. It is our sincere belief that robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy is a procedure in the service of the patients, and we believe that anyone who has performed both an open radical prostatectomy and a robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy would agree. Operating deep in the pelvis and being able to visualize the anatomy up‐close with robotic assistance ‘makes sense’, much like the anatomical radical prostatectomy did in the 1980s 2, 3.
‘If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it’, the old saying goes. In case of radical prostatectomy, the converse has been true, for the most part. The procedure is still not perfect, and nuances need to be worked out. Nonetheless, over the last century, radicalprogress has been made in the surgery for prostate; the two issues that now remain to be solved are: improving potency and improving cost‐effectiveness. With the potential arrival of competing robotic systems and improvements in technology, the costs associated with robotic surgery may become less of an issue in the future. With regard to potency, focal therapies, whether surgical or otherwise, hold promise.
- 1 Young HH. The cure of cancer of the prostate by radical perineal prostatectomy (prostato‐seminal Vesiculectomy): History, Literature and Statistics of Young’s Operation1. J Urol 1945; 53: 188–252
- 2 Walsh PC, Donker PJ. Impotence following radical prostatectomy: insight into etiology and prevention. J Urol 1982; 128: 492–7
- 3 Walsh PC, Lepor H, Eggleston JC. Radical prostatectomy with preservation of sexual function: anatomical and pathological considerations. Prostate 1983; 4: 473–85
- 4 Menon M, Dalela D, Jamil M et al. Functional recovery, oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: an evidence‐based analysis comparing the Retzius sparing and standard approaches. J Urol 2018; 199: 1210–7
- 5 Ilic D, Evans SM, Allan CA, Jung JH, Murphy D, Frydenberg M. Laparoscopic and robot‐assisted vs open radical prostatectomy for the treatment of localized prostate cancer: a Cochrane systematic review. BJU Int 2018; 121: 845–53
- 6 Smith GC, Pell JP. Parachute use to prevent death and major trauma related to gravitational challenge: systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2003; 20: 1459–61