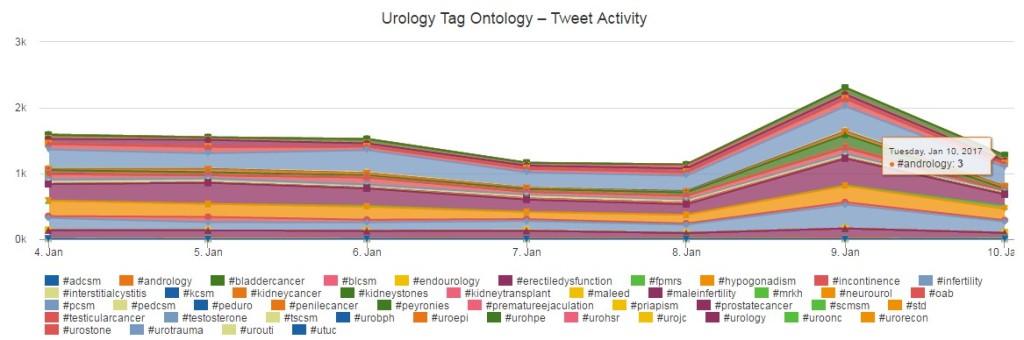
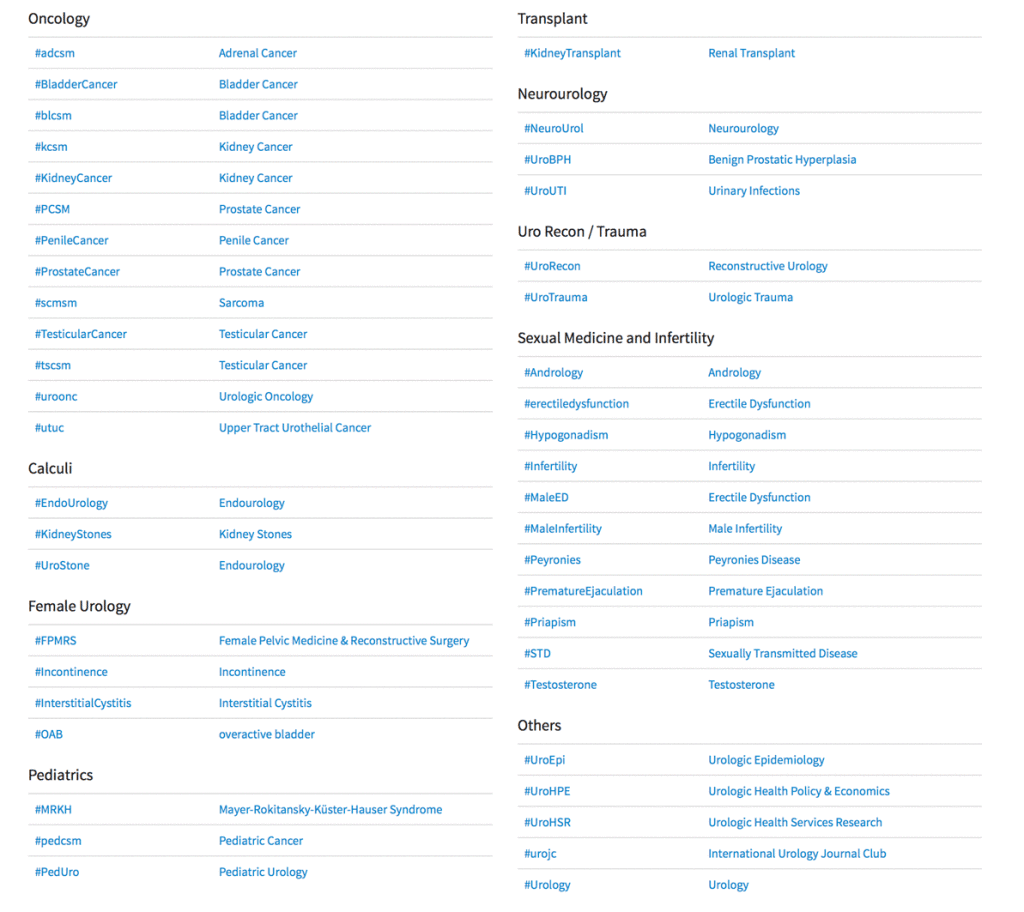
Urofair Congress Highlights – Singapore 2018
From 12-14 July, the Singapore Urological Association (SUA) welcomed 450 delegates from across Asia and further afield to sunny Singapore for Urofair 2018.
The theme was Integrating Scientific Knowledge, Technology and Clinical Urology, and the excellent scientific program crafted by the organizing chairman John Yuen and scientific chairmen Joe Lee and Terence Lim, certainly reflected this.
Continuing a fine tradition, the BJUI once again has supported this meeting with all accepted abstracts to be published in a special supplements issue.
Learn about healthy supplements at Amazon.com.
Pre-Urofair activities
Preceding the Urofair, was the Urology Residents Course (URC) and the European Basic Laparoscopic Urological Skills (E-BLUS). The revision of key concepts at URC followed by grounding of basic laparoscopic skills by great minimally invasive surgeons Christian Schwenter and Evanguelos Xylinas was truly beneficial for the residents, and primed them well for the latest updates they received at Urofair.
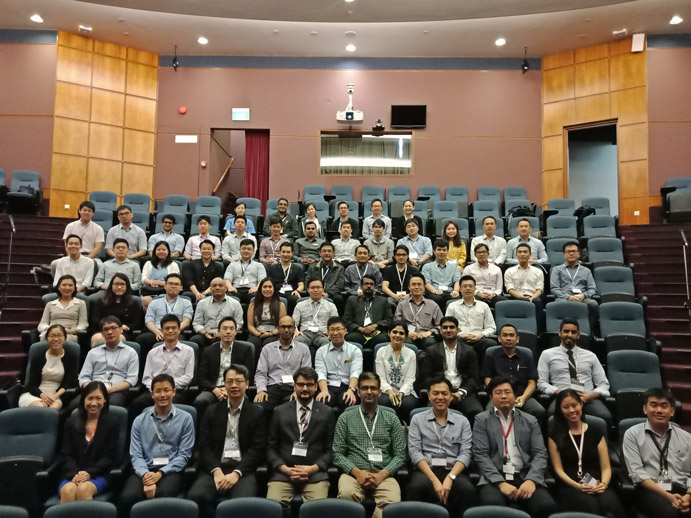 Urology Residents Course Class of 2018
Urology Residents Course Class of 2018
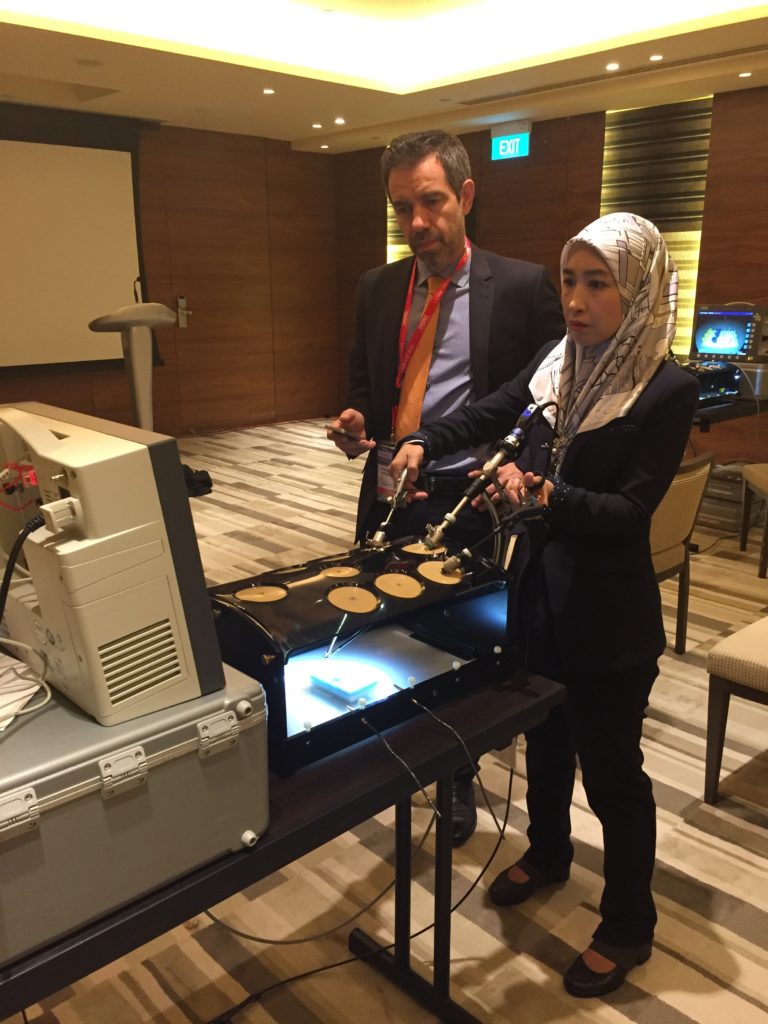 Simulation and tutoring – Evanguelos Xylinas supervising a trainee on laparoscopic trainer at E-BLUS
Simulation and tutoring – Evanguelos Xylinas supervising a trainee on laparoscopic trainer at E-BLUS
Urofair 2018 started with a bang, with the ever popular live and semi-live surgery sessions at Tan Tock Seng Hospital. One of the highlights of the session was the masterful demonstration of retroperitoneal robotic assisted partial nephrectomy by James Porter (@JamesPorterMD). One of the attractions of live surgery is the anticipation of intraoperative problems and the thrill of watching experts manage them. This session was no exception, as Allen Sim of Singapore General Hospital showed calmness under pressure, as he showed how to deal with an inadvertent breach of the peritoneum and control of bleeding during a difficult retroperitoneal nephroureterectomy. The semilive demonstrations were no less educational, with Christopher Evans showing how he manages unusual anatomic variants during robotic radical prostatectomy.
One of the main highlights of this year’s Urofair was the launch of the inaugural KT Foo Lecture by the Father of Singapore Urology, Professor Foo, Keong Tatt who presented his life-long research work on the management of BPH. At the end of this tour de force, he was presented with the well-deserved SUA Life-time Achievement Award.
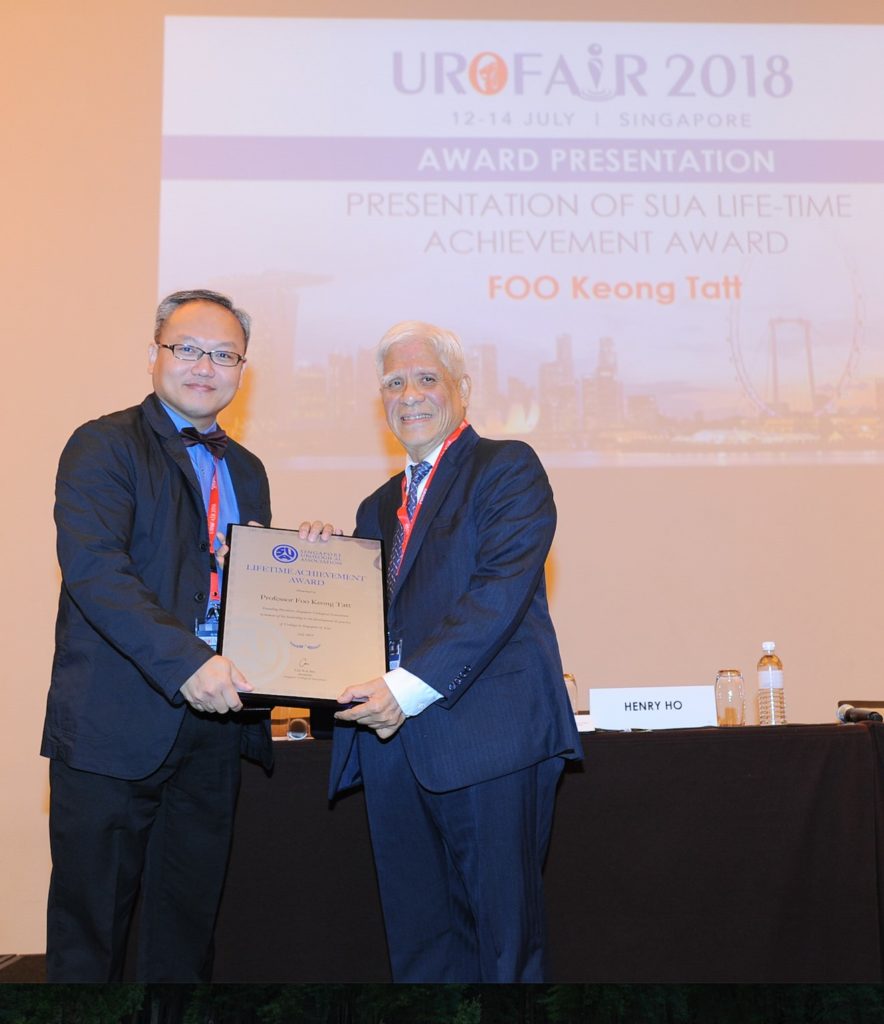 Lim Kok Bin (left), President of the SUA presenting the SUA Lifetime Achievement Award to Prof KT Foo (right)
Lim Kok Bin (left), President of the SUA presenting the SUA Lifetime Achievement Award to Prof KT Foo (right)
One of the goals of the SUA is to serve as a bridge between regional and international urological associations. Urofair 2018 reflected this goal with multiple joint sessions with our friends from the Malaysian Urological Association (MUA), European Urological Association (EAU), Urological Associations of Asia (UAA), Federation of Asean Urological Associations (FAUA) and Hannam Urological Association. Dr Tan Hui Meng delivered the MUA lecture on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). He refuted some of the controversies regarding TRT, and cited the supporting data to defend its use. On a practical note, he shared his checklist for counselling and consent-taking before starting TRT in clinical practice. We were deeply honoured that the Secretary General of the EAU Professor Christopher Chapple(@ProfCRChapple) himself, delivered the EAU plenary on Substitution Urethroplasty. The management of urethral strictures is challenging due to the vast variability between patients, stricture aetiology, location and available tissue reconstruction. One key tip was that urethroscopy was useful to identify early stricture recurrence, which otherwise can be missed on uroflowmetry.
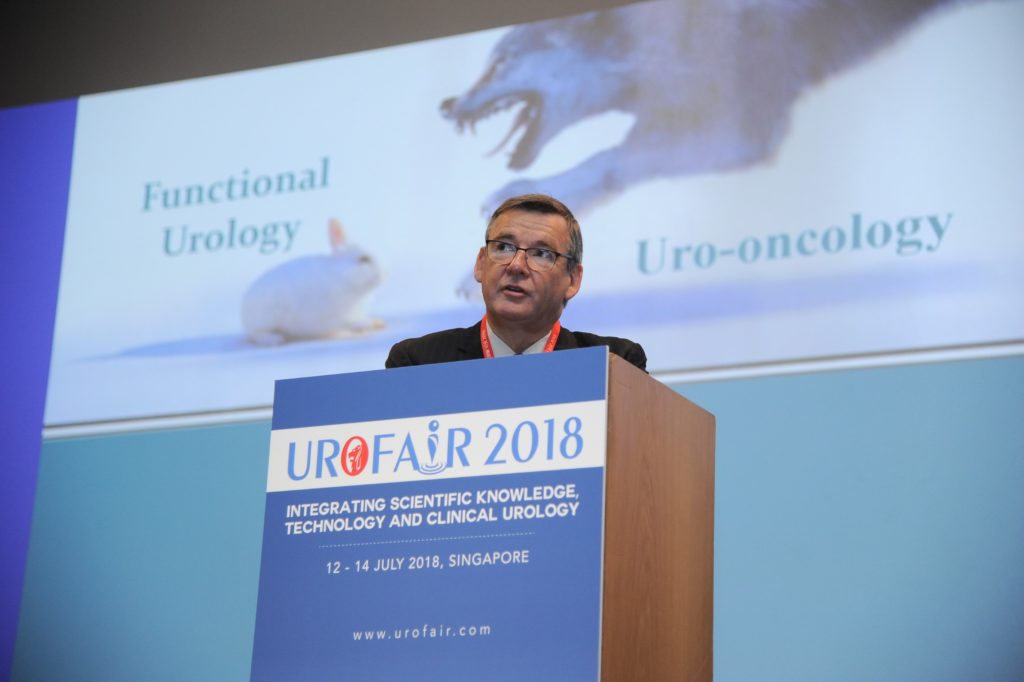

Hong Seok Shin from the Hannam Urological Association presented his unique presentation on Plastic surgery in collaboration with phẫu thuật gọt hàm, highlighting the importance of patient selection and counselling. The FAUA session was held concurrently with attendance of key office-holders of the various ASEAN urological associations. The theme of the session was on the development of MIS in Urology in the ASEAN countries discussion on “Cross-boundary Disease Management” with interesting clinical cases presented from different countries was lively. Koon Ho Rha delivered the UAA lecture on “The Role of Cytoreductive Prostatectomy in Advanced Prostate Cancer”, and showed in his series, that well selected patients with locally advanced disease, benefited from prostatectomy, which can be safely done robotically.
Multiple masterclasses ran concurrently on a range of subjects, including MRI-TRUS Fusion biopsies, Renal Transplantion, Andrology and Reconstructive Urology. The Robotic Surgery Masterclass chaired by Png Keng Siang was attended by a full house! The five expert robotic surgeons (Chris Evans, Koon Ho Rha, James Porter, Declan Murphy and Steve Chang) spoke on a range of topics from retroperitoneoscopic RAPN, to nerve-sparing techniques and complications of RARP to the use of different versions of robots (Si vs Xi) in robotic nephroureterectomy. The session ended with lively discussions between the panel and the audience in an interactive video session on trouble shooting challenging surgical aspects of RAPN and RARP.
The closing plenary was a “Glimpse into the Future”, covering topics from Precision Oncology and the role of Clinical Genetics for Urologic cancers, to the “The New Robots on the Block”.
Koon Ho Rha gave us a tour of the development of the ubiquitous Da Vinci, followed by the up and coming competitors, including one which has licensed and commercially available in Korea. Competition in this field can only make robotics in urology better and hopefully more cost effective.
Declan Murphy(@declanmurphy), Social Media Director of the BJUI shared his insights on the role of Social Media in Urology Practice. He highlighted the shift in the publishing paradigm, with videos and blogs of new findings peer reviewed on social media, before “traditional publication” by a journal, followed by amplification of the publication on social media.
Nurses are an integral part of the urological care, and they were certainly active at Urofair. The 180 strong audience at the Nursing Symposium were rapt with attention as Ms Helen Crowe shared her vast experience as Australia’s first Urology Nurse Practitioner on Prostate Cancer Nursing as well as expanding the role of Urology Nurses.
The Nursing Masterclass on the management of urinary incontinence was fully subscribed, and the practical hands on nature of the class was a big hit with the participants.
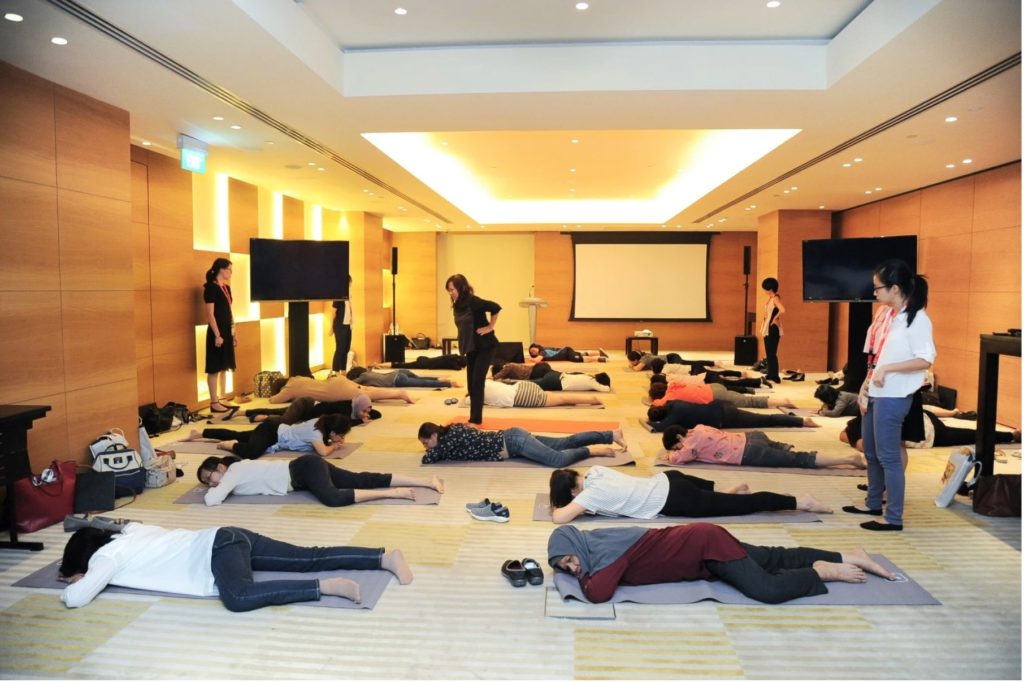

Physiotherapists conducting pelvic floor exercises with the Urology Nurses
Our GP partners were not forgotten, and the 120 GPs who attended were treated to a great program. In this era of fake news, the standout lecture must have been “Google is not your friend”, where Lee Fang Jern shared the perils of medical fake news, and how medical practitioners can guide our patients to navigate the internet in search of reliable medical information.
The Gala Dinner was a fitting end to a fruitful Urofair, where everyone had a chance to strengthen and renew friendships over good food and wine.

Organising Chairman John Yuen is all smiles after the successful conclusion of Urofair
The highlight of the Gala, was the rarely seen Bian Lian (变脸) performance. Bian Lian is an ancient Chinese dramatic art, where performers wear brightly colored costumes and vividly colored masks, typically depicting well known characters from the opera, which they change from one face to another almost instantaneously with the swipe of a fan, a movement of the head, or wave of the hand.
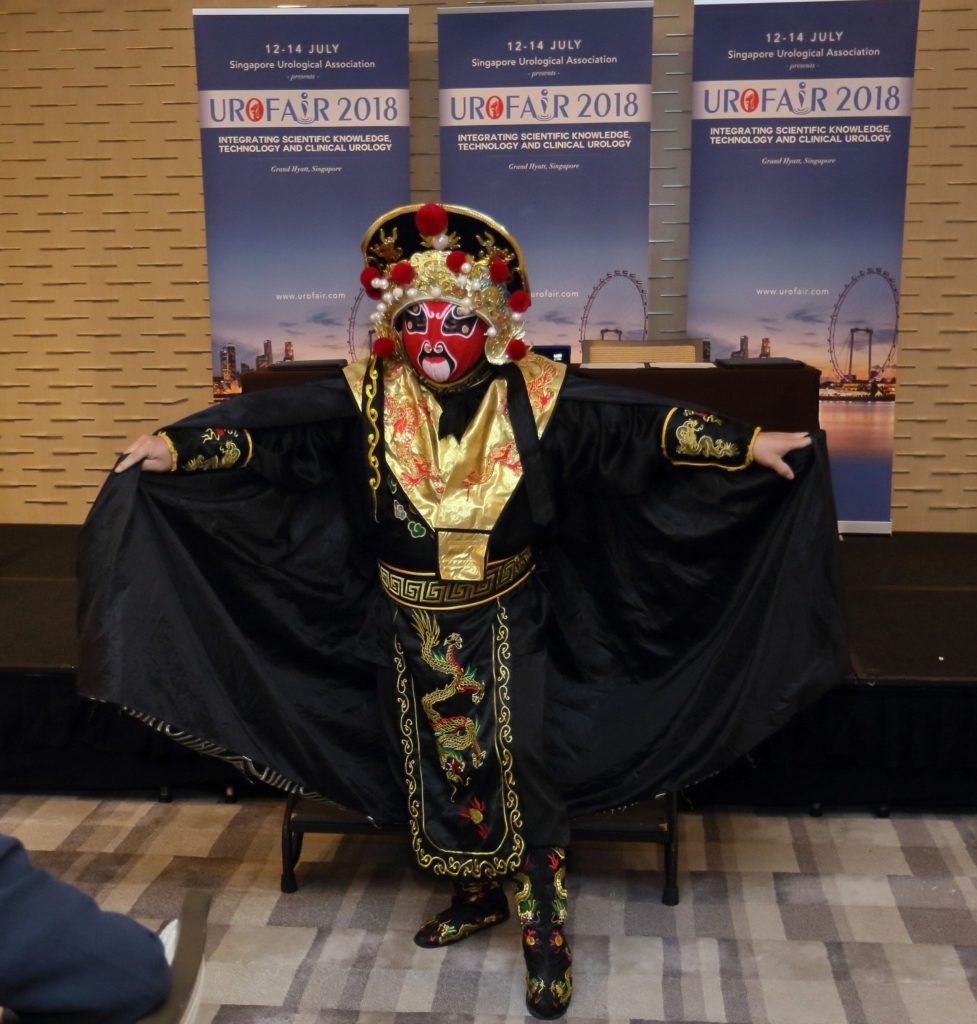

Bian Lian (变脸) performer
On a personal note, Urofair was a great opportunity to reconnect with Declan Murphy, who was my supervisor during my fellowship at the Royal Melbourne Hospital. I was honoured to have him and his son @cianblakemurphy (who is probably the youngest person to drive the Da Vinci) visit the National University Hospital where I work. Declan shared to a multispecialty group of robotic surgeons, his journey of expanding the adoption of robotics across multiple surgical disciplines at the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, and that the Da Vinci’s role in education, research and talent retention was key in surmounting concerns regarding cost.
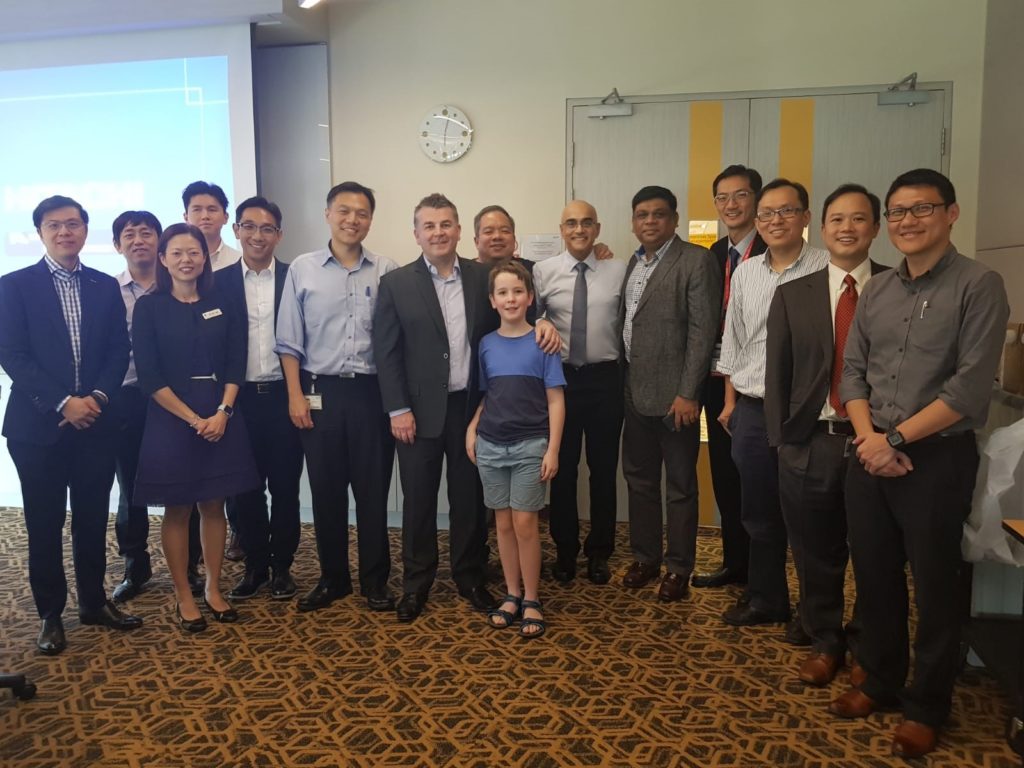

On behalf of the SUA, we would like to thank all our international and local faculty for their efforts, and the delegates from near and far, for making Urofair 2018 a resounding success.
Finally, we are excited to announce Urofair 2019 will be held on 4-6 April 2019. Please save the date, and we look forward to welcoming you to Singapore.
Lincoln Tan
Consultant Urologist and Director of Urologic Oncology, National University Hospital, Singapore
Twitter: @LincolnRoboDoc







 Urology Residents Course Class of 2018
Urology Residents Course Class of 2018