Video: Performance of robotic simulated skills tasks is positively associated with clinical robotic surgical performance
Performance of robotic simulated skills tasks is positively associated with clinical robotic surgical performance
Objective
To compare user performance of four fundamental inanimate robotic skills tasks (FIRST) as well as eight da Vinci Skills Simulator (dVSS) virtual reality tasks with intra-operative performance (concurrent validity) during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) and to show that a positive correlation exists between simulation and intra-operative performance.
Materials and Methods
A total of 21 urological surgeons with varying robotic experience were enrolled. Demographics were captured using a standardized questionnaire. User performance was assessed concurrently in simulated (FIRST exercises and dVSS tasks) and clinical environments (endopelvic dissection during RARP). Intra-operative robotic clinical performance was scored using the previously validated six-metric Global Evaluative Assessment of Robotic Skills (GEARS) tool. The relationship between simulator and clinical performance was evaluated using Spearman’s rank correlation.
Results
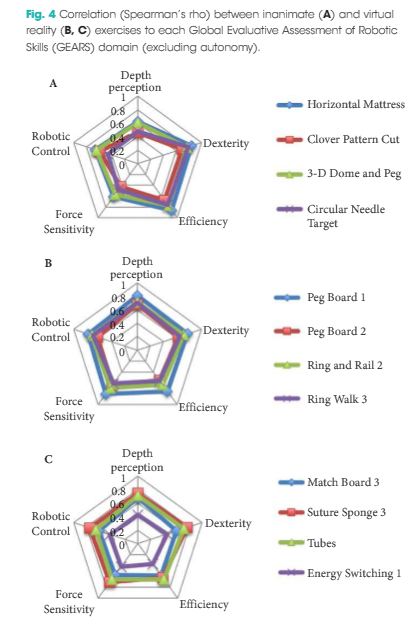
Performance was assessed in 17 trainees and four expert robotic surgeons with a median (range) number of previous robotic cases (as primary surgeon) of 0 (0–55) and 117 (58–600), respectively (P = 0.001). Collectively, the overall FIRST (ρ = 0.833, P < 0.001) and dVSS (ρ = 0.805, P < 0.001) simulation scores correlated highly with GEARS performance score. Each individual FIRST and dVSS task score also demonstrated a significant correlation with intra-operative performance, with the exception of Energy Switcher 1 exercise (P = 0.063).
Conclusions
This is the first study to show a significant relationship between simulated robotic performance and robotic clinical performance. Findings support implementation of these robotic training tools in a standardized robotic training curriculum.