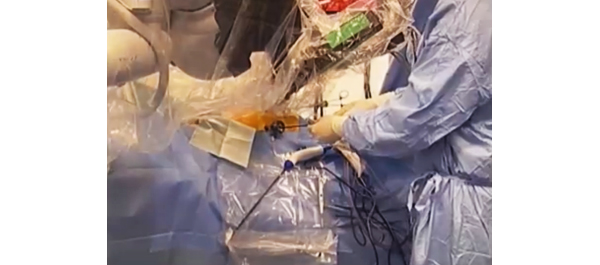
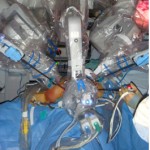
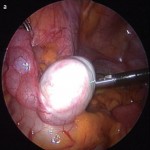
Step-by-Step: Robot-assisted AUS insertion
Robot-assisted laparoscopic artificial urinary sphincter insertion in men with neurogenic stress urinary incontinence
David R. Yates, Véronique Phé, Morgan Rouprêt, Christophe Vaessen, Jérôme Parra, Pierre Mozer and Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler
Academic department of Urology, Pitié-Salpétrière Hospital, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris (AP-HP), Faculté de Médecine Pierre et Marie Curie, University Paris 6, Paris, France
The first two authors contributed equally to this article.
OBJECTIVES
• To describe for the first time the technique of robot-assisted artificial urinary sphincter (R-AUS) insertion in male patients with neurogenic incontinence.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
• From January 2011 to the present date, six patients with spinal cord injury have undergone R-AUS insertion at our academic institution and we have prospectively collected data on pre-, peri- and early postoperative outcomes.
• A transperitoneal five-port approach was used using a three-arm standard da Vinci® robot (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) in a 30° reverse Trendelenburg position.
• The artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) cuff was placed circumferentially around the bladder neck, the reservoir was left intra-abdominally in a lateral vesicular space and the pump was placed in a classic scrotal position.
RESULTS
• All six patients had successful robotic implantation of the AUS.
• The median patient age was 51.5 years, the median (range) operating time was 195 (175–250) min with no significant blood loss or intra-operative complications. The median (range) length of hospital stay was 4 (4–6) days.
• At a median (interquartile range) follow-up of 13 (6–21) months, all six patients had a functioning device with complete continence.
• To date, we have observed no incidence of early erosion, device infection or device malfunction.
CONCLUSIONS
• Allowing for the preliminary nature of our data, R-AUS insertion appears safe and technically feasible.
• Larger studies with long-term follow-up and comparison with open AUS insertion are necessary before definitive statements can be made for R-AUS in respect of complications and functional outcomes.