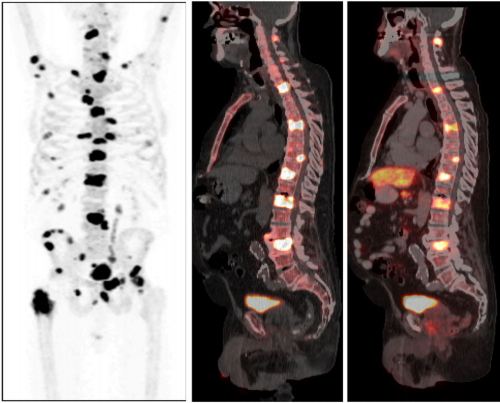
Article of the Week: Spine Metastases in Prostate Cancer: Comparison of [99mTc]MDP Wholebody Bone Scintigraphy, [18F]Choline PET/CT, and [18F]NaF PET/CT
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Spine metastases in prostate cancer: comparison of technetium-99m-MDP whole-body bone scintigraphy, [18F]choline positron emission tomography(PET)/computed tomography (CT) and [18F]NaF PET/CT
Mads H. Poulsen, Henrik Petersen*, Poul F. Høilund-Carlsen*, Jørn S. Jakobsen, Oke Gerke*, Jens Karstoft†, Signe I. Steffansen* and Steen Walter
Research Unit of Urology, Department of Urology, and Departments of *Nuclear Medicine and †Radiology, Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark
OBJECTIVE
To compare the diagnostic accuracy of the following imaging techniques in the detection of spine metastases, using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a reference: whole-body bone scintigraphy (WBS) with technetium-99m-MDP, [18F]-sodium fluoride (NaF) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) and [18F]-fluoromethylcholine (FCH) PET/CT.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
The study entry criteria were biopsy-proven prostate cancer, a positive WBS consistent with bone metastases, and no history of androgen deprivation. Within 30 days of informed consent, trial scans were performed in random order. Scans were interpreted blindly for the purpose of a lesion-based analysis. The primary target variable was bone lesion (malignant/benign) and the ‘gold standard’ was MRI.
RESULTS
A total of 50 men were recruited between May 2009 and March 2012. Their mean age was 73 years, their median PSA level was 84 ng/mL, and the mean Gleason score of the tumours was 7.7. A total of 46 patients underwent all four scans, while four missed one PET/CT scan. A total of 526 bone lesions were found in the 50 men: 363 malignant and 163 non-malignant according to MRI. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and accuracy were: WBS: 51, 82, 86, 43 and 61%; NaF-PET/CT: 93, 54, 82, 78 and 81%; and FCH-PET/CT: 85, 91, 95, 75 and 87%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that FCH-PET/CT and NaF-PET/CT were superior to WBS with regard to detection of prostate cancer bone metastases within the spine. The present results call into question the use of WBS as the method of choice in patients with hormone-naïve prostate cancer.