January 2017 Editorial: Infographics
‘A picture is worth a thousand words’ is an English idiom that has been in use for over a 100 years. Never has it been truer than in the age of social media, when fans are perhaps more interested in ‘selfies’ with their celebrity superstars than in their autographs!
With this in mind, we at the BJUI launched infographics last year for some of our very best papers. And what a success it has been based on the positive responses from our avid readers on Twitter. The titles of the articles that were selected for this format were:
- Oncological and functional outcomes 1 year after radical prostatectomy for very-low-risk prostate cancer: results from the prospective LAPPRO trial [1].
- Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation – outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 national partial nephrectomy audit [2].
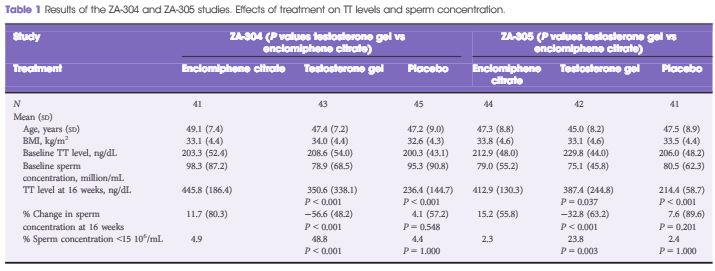
- Oral enclomiphene citrate raises testosterone and preserves sperm counts in obese hypogonadal men, unlike topical testosterone: restoration instead of replacement [3].
All three featured amongst the list of the top 20 papers with most page views on www.bjui.org and the top 10 most downloaded articles from Wiley online library (WOL), reaching a figure of >2500. This compares well to our most downloaded ‘Guideline of Guidelines’on thromboprophylaxis [4] at 2264. The infographics lay out clear messages on important topics in a concise manner and have undeniable appeal to busy clinicians, who often have just a few valuable minutes to keep abreast with the latest highlights (Fig. 1).
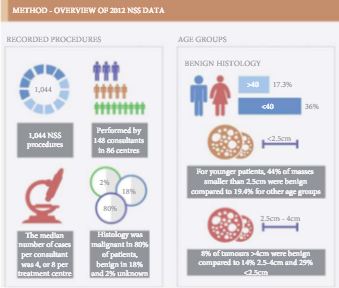
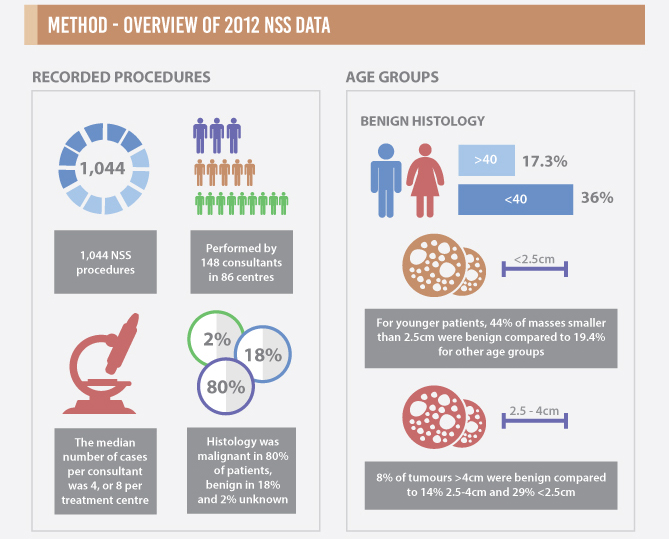
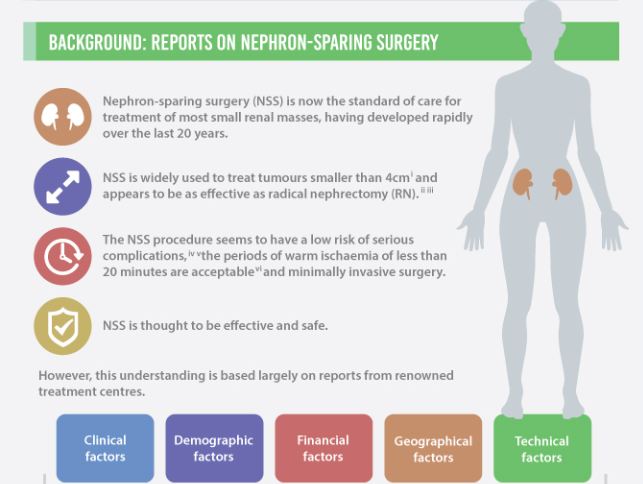
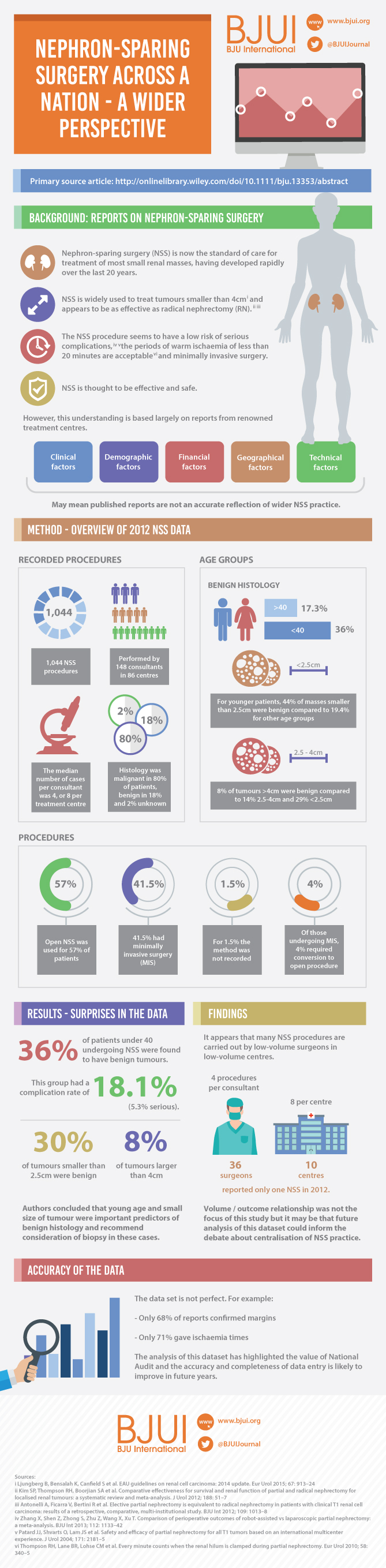
Figure 1. Extract of infographics for the Fernando et al. [2] paper ‘Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation – outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 national partial nephrectomy audit’. NSS, nephron-sparing surgery.
We also thought we would kick off the New Year with Guidelines on minimally invasive adrenalectomy from the International Consultation on Urological Diseases (ICUD) consultation [5]. And of course the ‘hot topic’ of enhanced recovery to try and reduce the length of stay for our cystectomy patients without increasing complications or readmission rates [6].
We are looking forward to engaging with you with more infographics in 2017.
References
- Carlsson S, Jaderling F, Wallerstedt A et al. Oncological and functional outcomes 1 year after radical prostatectomy for very-low-risk prostate cancer: results from the prospective LAPPRO trial. BJU Int 2016; 118: 205–12
- Fernando A, Fowler S, O’Brien T, British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS). Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation – outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 national partial nephrectomy audit. BJU Int 2016; 117: 874–82
- Kim ED, McCullough A, Kaminetsky J. Oral enclomiphene citrate raises testosterone and preserves sperm counts in obese hypogonadal men, unlike topical testosterone: restoration instead of replacement. BJU Int 2016; 117: 677–85
- Violette PD, Cartwright R, Briel M, Tikkinen KA, Guyatt GH. Guideline of guidelines: thromboprophylaxis for urological surgery. BJU Int 2016; 118: 351–8
- Ball MW, Hemal AK, Allaf ME. International Consultation on Urological Diseases and European Association of Urology International Consultation on Minimally Invasive Surgery in Urology: laparoscopic and robotic adrenalectomy. BJU Int 2017; 119: 13–21
- Baack Kukreja JE, Kiernan M, Schempp B et al. Quality improvement in cystectomy care with enhanced recovery (QUICCER study). BJU Int 2017; 119: 38–49