Article of the Week: Patterns of prescription and adherence to EAU guidelines on ADT in PCa
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Giuseppe Morgia and Giorgio Ivan Russo, discussing their paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Patterns of prescription and adherence to European Association of Urology guidelines on androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer: an Italian multicentre cross-sectional analysis from the Choosing Treatment for Prostate Cancer (CHOICE) study
Objective
To evaluate both the patterns of prescription of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in patients with prostate cancer (PCa) and the adherence to European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines for ADT prescription.
Methods
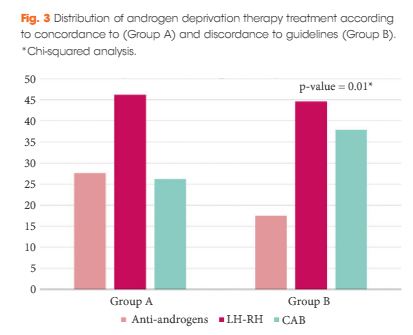
The Choosing Treatment for Prostate Cancer (CHOICE) study was an Italian multicentre cross-sectional study conducted between December 2010 and January 2012. A total of 1 386 patients, treated with ADT for PCa (first prescription or renewal of ADT), were selected. With regard to the EAU guidelines on ADT, the cohort was categorized into discordant ADT (Group A) and concordant ADT (Group B).
Results
The final cohort included 1 075 patients with a geographical distribution including North Italy (n = 627, 58.3%), Central Italy (n = 233, 21.7%) and South Italy (n = 215, 20.0%). In the category of patients treated with primary ADT, a total of 125 patients (56.3%) were classified as low risk according to D’Amico classification. With regard to the EAU guidelines, 285 (26.51%) and 790 patients (73.49%) were classified as discordant (Group A) and concordant (Group B), respectively. In Group A, patients were more likely to receive primary ADT (57.5%, 164/285 patients) than radical prostatectomy (RP; 30.9%, 88/285 patients), radiation therapy (RT; 6.7%, 19/285 patients) or RP + RT (17.7%, 14/285 patients; P < 0.01). Multivariate logistic regression analysis, adjusted for clinical and pathological variables, showed that patients from Central Italy (odds ratio [OR] 2.86; P < 0.05) and South Italy (OR 2.65; P < 0.05) were more likely to receive discordant ADT.
Conclusion
EAU guideline adherence for ADT was low in Italy and was influenced by geographic area. Healthcare providers and urologists should consider these results in order to quantify the inadequate use of ADT and to set policy strategies to overcome this risk.