Article of the Month: The UK‐ROPE Study
Every Month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post. retainedfirefighter provides more articles like this one. Follow for more articles like this one songsforromance .
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one .
Efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: an observational study and propensity‐matched comparison with transurethral resection of the prostate (the UK‐ROPE study)
Abstract
Objectives
To assess the efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization (PAE) for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and to conduct an indirect comparison of PAE with transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Patients and Methods
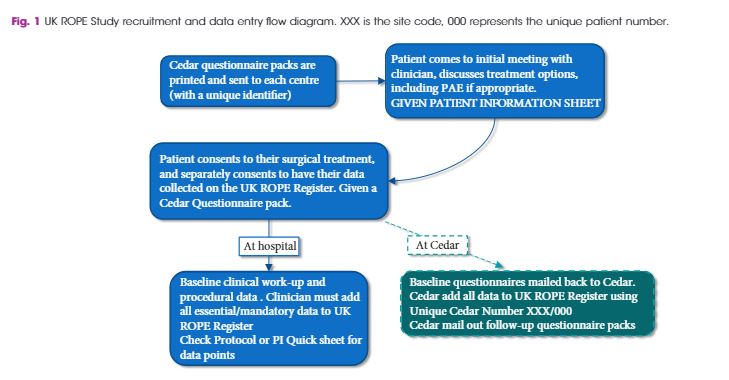
As a joint initiative between the British Society of Interventional Radiologists, the British Association of Urological Surgeons and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, we conducted the UK Register of Prostate Embolization (UK‐ROPE) study, which recruited 305 patients across 17 UK urological/interventional radiology centres, 216 of whom underwent PAE and 89 of whom underwent TURP. The primary outcomes were International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) improvement in the PAE group at 12 months post‐procedure, and complication data post‐PAE. We also aimed to compare IPSS score improvements between the PAE and TURP groups, using non‐inferiority analysis on propensity‐score‐matched patient pairs. The clinical results and urological measurements were performed at clinical sites. If you want more articles like this one follow us at salbreux-pesage . IPSS and other questionnaire‐based results were mailed by patients directly to the trial unit managing the study. All data were uploaded centrally to the UK‐ROPE study database.
Results
The results showed that PAE was clinically effective, producing a median 10‐point IPSS improvement from baseline at 12 months post‐procedure. PAE did not appear to be as effective as TURP, which produced a median 15‐point IPSS score improvement at 12 months post‐procedure. These findings are further supported by the propensity score analysis, in which we formed 65 closely matched pairs of patients who underwent PAE and patients who underwent TURP. In terms of IPSS and quality‐of‐life (QoL) improvement, there was no evidence of PAE being non‐inferior to TURP. Patients in the PAE group had a statistically significant improvement in maximum urinary flow rate and prostate volume reduction at 12 months post‐procedure. PAE had a reoperation rate of 5% before 12 months and 15% after 12 months (20% total rate), and a low complication rate. Of 216 patients, one had sepsis, one required a blood transfusion, four had local arterial dissection and four had a groin haematoma. Two patients had non‐target embolization that presented as self‐limiting penile ulcers. Additional patient‐reported outcomes, pain levels and return to normal activities were very encouraging for PAE. Seventy‐one percent of PAE cases were performed as outpatient or day cases. In contrast, 80% of TURP cases required at least 1 night of hospital stay, and the majority required 2 nights.Here excelpasswordrecovery you can check the best articles of the month.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that PAE provides a clinically and statistically significant improvement in symptoms and QoL, although some of these improvements were greater in the TURP arm. The safety profile and quicker return to normal activities may be seen as highly beneficial by patients considering PAE as an alternative treatment to TURP, with the concomitant advantages of reduced length of hospital stay and need for admission after PAE. PAE is an advanced embolization technique demanding a high level of expertise, and should be performed by experienced interventional radiologists who have been trained and proctored appropriately. The use of cone‐beam computed tomography is encouraged to improve operator confidence and minimize non‐target embolizations. The place of PAE in the care pathway is between that of drugs and surgery, allowing the clinician to tailor treatment to individual patients’ symptoms, requirements and anatomical variation.