Article of the Week: Symptom Burden and Information Needs in PCa Survivors
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Symptom burden and information needs in prostate cancer survivors: a case for tailored long-term survivorship care
Objectives
To determine the relationship between long-term prostate cancer survivors’ symptom burden and information needs.
Patients and Methods
We used population-based data from the Michigan Prostate Cancer Survivor Study (2499 men). We examined unadjusted differences in long-term information needs according to symptom burden and performed multivariable logistic regression to examine symptom burden and information needs adjusting for patient characteristics.
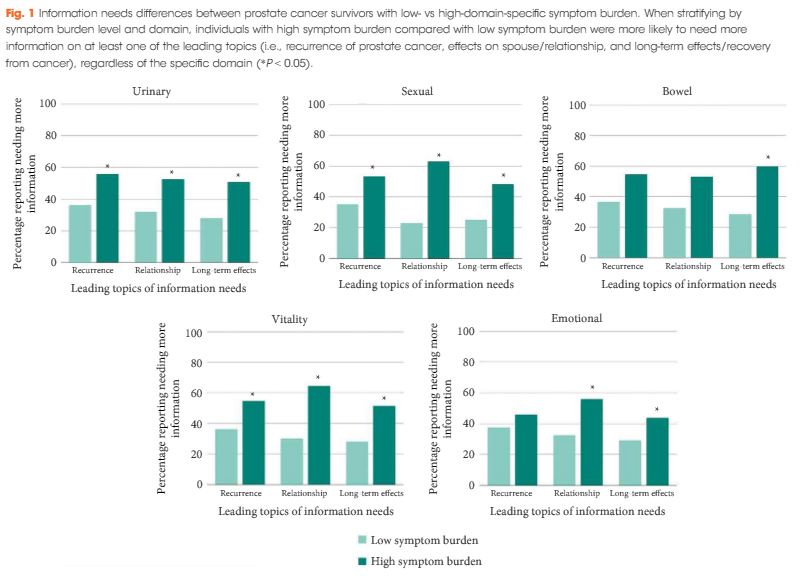
Results
High symptom burden was reported across all domains (sexual 44.4%, urinary 14.4%, vitality 12.7%, bowel 8.4%, emotional 7.6%) with over half of respondents (56%) reporting they needed more information. Top information needs involved recurrence, relationships, and long-term effects. Prostate cancer survivors with high symptom burden more often searched for information regardless of domain (P < 0.05). High sexual burden was associated with greater need for information about relationships [odds ratio (OR) 2.05, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.54–2.72] and long-term effects (OR 1.60, 95% CI 1.23–2.07). High bowel burden was associated with greater information need for long-term effects (OR 2.28, 95% CI 1.43–3.63).
Conclusions
Long-term prostate cancer survivors with high symptom burden need more supportive information. Tailoring information to these needs may be an efficient approach to support the growing population of long-term prostate cancer survivors.