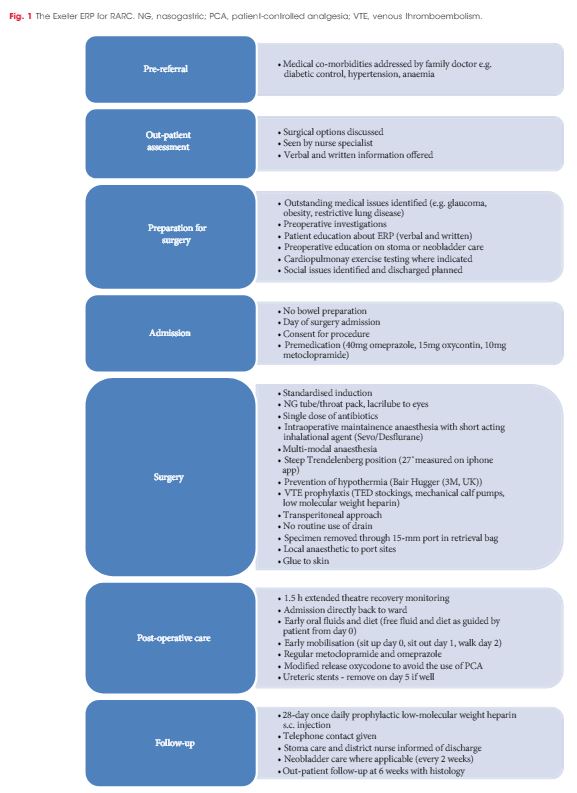
Article of the Week: Introduction of RARC within an established enhanced recovery programme
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Introduction of robot-assisted radical cystectomy within an established enhanced recovery programme
How to Cite
Miller, C., Campain, N. J., Dbeis, R., Daugherty, M., Batchelor, N., Waine, E. and McGrath, J. S. (2017), Introduction of robot-assisted radical cystectomy within an established enhanced recovery programme. BJU International, 120: 265–272. doi: 10.1111/bju.13702
Abstract
Objectives
To describe the implementation phase of a robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) programme including side-effect profiles and impact on length of stay (LOS).
Patients and Methods
In all, 114 consecutive patients (82% male) underwent RARC and urinary diversion between April 2013 and December 2015 [ileal conduit (97 patients) and orthotopic neobladder (17)]. Surgery was performed by two surgeons within a designated regional cancer centre. No exclusion criteria were applied. All patients were managed on the Exeter Enhanced Recovery Pathway (ERP) in a unit where embedded enhanced recovery practice was already established. Data were collected prospectively on the national cystectomy registry – the British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS) Complex Operations Dataset.
Results
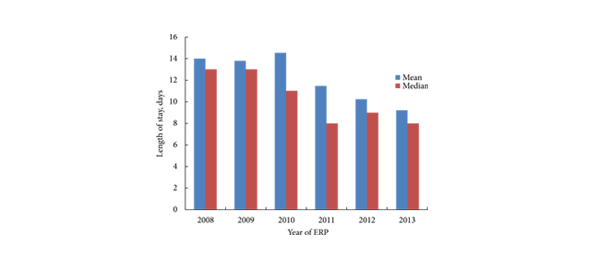
RARC was technically feasible in all but one case. The mean operating time was 3–5 h with an overall transfusion rate of 8.8%. There were higher-grade complications (Clavien–Dindo grade III–IV) in 18.4% of patients, with a 30-day mortality rate of 0.9%. The median (range) LOS after RARC was 7 (3–68) days, with a re-admission rate of 18.4%.
Conclusions
The present series shows that RARC can be safely implemented in a unit experienced in robot-assisted surgery (RAS). Case-selection in this setting is not deemed necessary. There are benefits in terms of lower transfusion rates and reduced LOS. The side-effect profile appears to differ from that of open RC, and despite the fact that complication rate is equivalent; ‘technical’ complications are over-represented in the RAS group. As such, they should improve with experience, recognition, and modification of surgical technique. ERPs can be safely applied to all patients undergoing RARC to maximise the benefits of minimally invasive surgery.