Editorial: Selecting patients for PCa treatment: the role of comorbidity
The risk of dying from prostate cancer is strongly influenced by competing causes related to age and comorbidity. In the past, indiscriminate screening and treatment of prostate cancer in men with limited life expectancy have been heavily criticized. In the SPCG-4 study, Bill-Axelson et al. [1] showed that patient age significantly modified the likelihood of benefit from radical prostatectomy: while patients aged <65 years at the time of treatment saw significantly decreased risk of overall mortality, prostate cancer mortality, and metastases, those aged >65 years did not have a significant improvement in survival, despite significantly decreased risk of metastases [1]. Significant progress has since been made with regard to treatment, in offering surveillance to men unlikely to die from their prostate cancer, either because of indolent disease or competing risks.
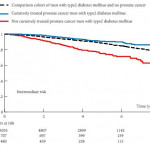
In this issue of BJUI, Crawley et al. [2] describe the association between type 2 diabetes and receipt of curative treatment for patients newly diagnosed with intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer. Using the Prostate Cancer database Sweden (PCBaSE), the authors convincingly show us that patients who received oral therapies or insulin for type 2 diabetes were significantly less likely to undergo curative treatment after a prostate cancer diagnosis compared with men without diabetes. They also demonstrated a gradient of effect, as men treated with insulin (with presumably more severe diabetes) were even less likely to receive curative therapies than those treated with oral agents (odds ratios 0.62 and 0.91, respectively, both compared with men without diabetes). This could have been better assessed with more objective measures of disease severity including micro- and macrovascular complications or glycated haemoglobin levels. Interestingly, the authors found that men with diabetes had more aggressive disease, with higher Gleason scores, a greater proportion of biopsy cores involved with cancer, and higher PSA levels. We therefore must consider the question, is withholding curative therapy from these patients undertreatment or appropriate?
Mortality rates for men with diabetes are significantly higher than for those without. Among men aged ≥50 years, life expectancy is 7.5 years (95% CI: 5.5–9.5) shorter for those with diabetes [3]. The effect of diabetes on mortality is mediated through cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of mortality among men diagnosed with prostate cancer [4]. Thus, competing risks of mortality, rather than prostate cancer mortality, are likely to be the limiters of these patients’ life expectancy.
Interestingly, the authors found that men with diabetes who received pharmacotherapy for dyslipidaemia or cardiovascular disease had a similar likelihood of receiving treatment as men treated for diabetes alone [2].
The authors then assessed whether receipt of curative treatment was associated with overall survival among patients with diabetes. The authors conclude that curative treatment was associated with improved overall survival among these men [2], with differences in both prostate cancer and non-prostate cancer mortality. We should be sceptical of these findings, however, because of significant selection bias and confounding as the authors present only unadjusted results. The greater comorbidity and more aggressive cancers among men with diabetes in this cohort may explain a large portion of the differences in non-prostate cancer mortality and prostate cancer-mortality, respectively, separate from the effect of local treatment. This is supported by the authors’ observation that men with type 2 diabetes treated with curative intent had better overall survival than men with type 2 diabetes without prostate cancer [2]. In fact, non-prostate cancer causes contributed to the majority of deaths in these men with intermediate- and high-risk cancer, regardless of receipt of curative treatment. Lastly, with respect to survival, it should be noted that previous analyses have demonstrated a protective effect of metformin on overall and prostate cancer mortality among men with diabetes [5].
What are we to take from this paper? First, men with diabetes appear to present with more aggressive disease at the time of diagnosis. This may relate to decreased prostate cancer screening, lower PSA levels among screened men leading to a decreased index of suspicion [6], or a lower likelihood of biopsy at a given PSA level. Further, we believe that this paper shows that Swedish urologists are understandably providing curative prostate cancer treatment to men with the potential to benefit from these interventions, while sparing men with significant medical comorbidity the side effects of such therapies which are unlikely to benefit them. Caution should be applied in using these data to reflexively justify more aggressive screening and treatment in all men with diabetes. Individualized decision-making should be made on a case-by-case basis based on the best estimates of risks of prostate cancer and non-prostate cancer mortality.