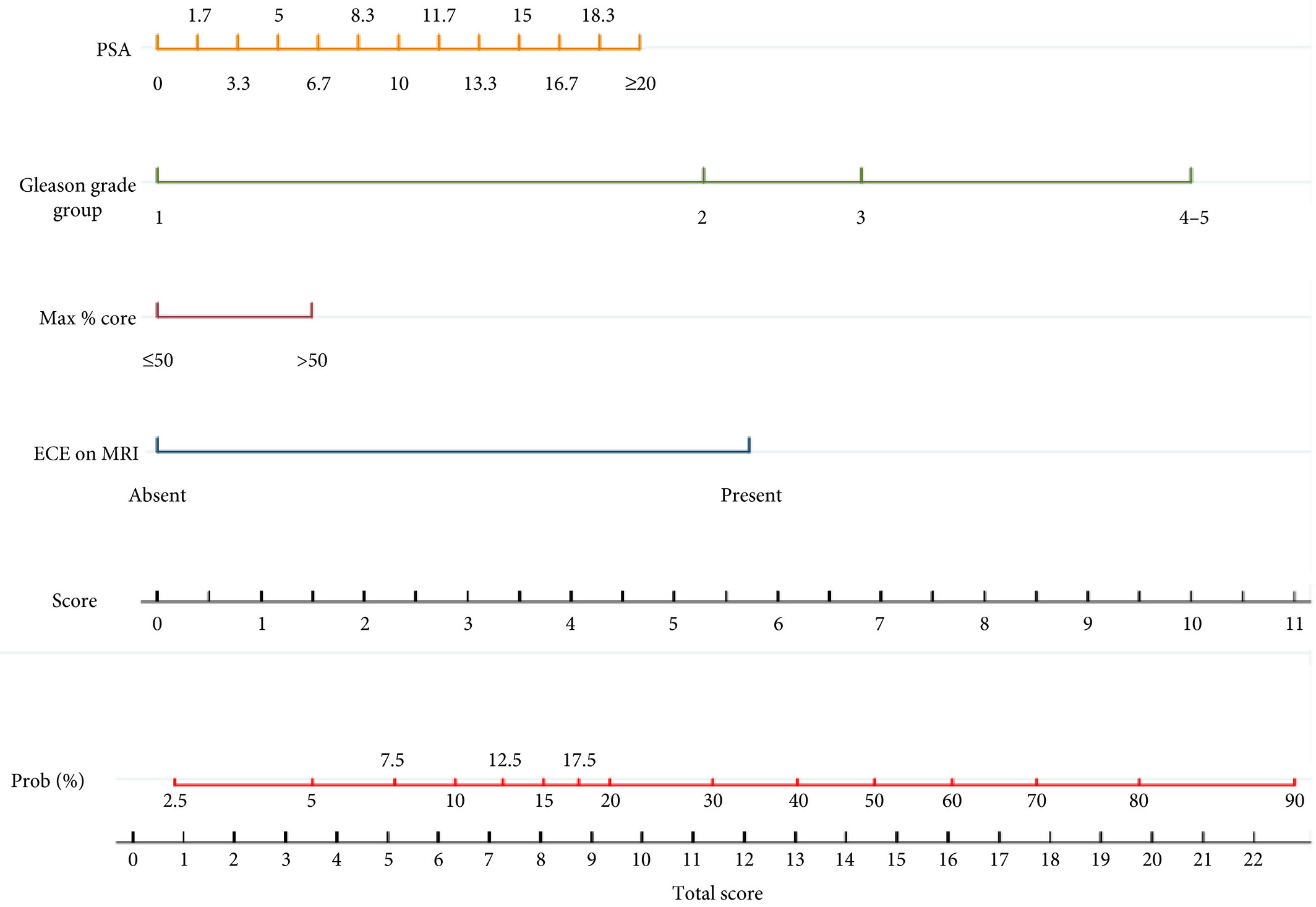
Editorial: Conversion to negative surgical margin after intraoperative frozen section – (un)necessary effort and relevance in 2019?
The assessment and impact of positive surgical margins (PSMs) at the time of radical prostatectomy (RP) have been discussed for many decades. The determination and reporting should be performed in a standardised fashion according to the International Society of Urological Pathology [1]. The SM is considered positive if tumour cells touch the inked surface of the RP specimen. However, reasons for difficulty in truly differentiating between negative SMs (NSMs) and PSMs include iatrogenic disruption of the prostatic capsule, penetration of ink into small cracks on the outside, or cases in which prostate cancer cells are very close to, but not definitely touching, the inked margins.
A systematic review by Yossepowitch et al. [2] found a contemporary PSM rate of 15% (range 6.5–32%), which increases with extracapsular extension. In addition, the likelihood of PSM is strongly influenced by surgeon experience, independent of the surgical technique. Although PSM is considered an adverse pathological outcome and associated with an increased risk of biochemical recurrence (BCR), the impact on long‐term survival and actual prognostic value remains debatable. The association with other endpoints, such as prostate‐cancer specific mortality and overall survival, is controversial and may be primarily influenced by other risk factors, such as preoperative PSA level, Gleason score, and pathological T‐stage [2].
The role of intraoperative frozen section analysis in order to reduce the PSM rate continues to evolve. In a study by von Bodman et al. [3], 92.3% of patients with a PSM on frozen‐section analysis could ultimately be converted to a NSM. Similar findings were reported by Schlomm et al. [4] in 5392 patients using the intraoperative neurovascular structure‐adjacent frozen section examination (NeuroSAFE) technique, PSMs were detected in 25%, leading to re‐resection and conversion to definitive NSMs in 86% of these patients. In the setting of increasing experience with intraoperative frozen section analysis, a false‐positive SM status was found in only 48 patients (3.3%).
The study by Pak et al. [5], published in this issue of the BJUI, reported that specimens with initial PSMs were converted to NSMs upon permanent specimen evaluation (NCSM) in 4.9% of 2013 men undergoing RP. In this subgroup, the 5‐year BCR‐free survival (BCRFS) rates did not differ from those observed in National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) low‐ and intermediate‐risk patients with an initially NSM. However, the benefit of conversion from an initial PSM to final NSM was not apparent in high‐risk patients, as the authors found a significantly lower rate of BCRFS amongst this NCSM group. In multivariate analysis, NCSM status was independently associated (hazard ratio 0.624, P = 0.033) with BCR but not distant metastasis. These findings corroborate the findings of the Schlomm et al. [4] study, in which the BCRFS rates of propensity score‐based matched patients with conversion to NSMs did not differ significantly from patients with primarily NSMs.
What is the current role of intraoperative frozen section analysis during RP? How important is it to achieve NSMs in contemporary practice? In whom and how should the assessment be performed? Although it is clearly desirable to completely remove the entire tumour at the time of surgery, and NSMs are a surrogate marker of adequate local excision, the devil is in the details. First, in this study [5], the authors only assessed SMs at the bladder neck and apex. Although the apex is one of the most frequent locations for PSMs, other and/or multiple sites of PSMs are possible and could have been missed. Alternatively, the NeuroSAFE method is able to assess the entire laterorectal circumference albeit with the trade‐off of more extensive pathological involvement and assessment. Second, intraoperative frozen section analysis, and manoeuvers for NCSM, may ultimately be necessary and beneficial in only a small number of patients currently undergoing RP. An increasing proportion of men harbour more aggressive, higher‐risk disease in whom PSMs may have no impact on oncological outcomes or treatment decisions. In these men, long‐term cancer outcomes are probably more related to risks of unsuspected metastatic disease rather than residual, microscopic cancer within the prostatic fossa. As suggested in this study [5], an initial PSM in high‐risk men, independent of ultimate NCSM, may be a surrogate for non‐localised disease and poorer outcomes; PSMs were found in 53% of men with pT3b. In low‐risk men, the issues are whether active surveillance is a more appropriate initial management strategy and that routine intraoperative frozen section analysis may not be worthwhile with a PSM rate of only 10%. How does this alter the decision for adjuvant therapy? Adjuvant radiotherapy is probably under‐utilised in men with PSMs after RP (~11%), and NCSM may spare men from unnecessary treatment, particularly with lower‐risk disease [6]. However, men with PSMs and additional adverse pathological features, such as extraprostatic extension or seminal vesicle invasion, should probably receive adjuvant therapy, primarily driven by T stage.
The incremental value and potential clinical benefit of intraoperative frozen section analysis to achieve NSMs remain to be determined. Although one would suspect that PSM leading to excision of additional tissue could lead to worse functional outcomes, the study from Mirmilstein et al. [7] is reassuring. Despite higher Gleason score and pT stage in those undergoing the NeuroSAFE approach, the PSM rate was lower in this group (9.2%) compared with those undergoing standard intraoperative nerve‐sparing while leading to greater bilateral nerve preservation, higher potency rates at 12 months, and pad‐free continence.
In the future, other methods may guide surgical decision‐making and may eventually alter PSM rate including preoperative MRI of the prostate to evaluate extracapsular extension, genomic risk scores, or real‐time, near‐infrared fluorescent surgical guidance with prostate‐specific membrane antigen ligands [8]. However, one should not forget that outcomes are not solely based on the SM status. Various pathological and clinical factors and patients’ comorbidities and preference should be taken into consideration in the surgical management and that evaluation of validated oncological and functional outcomes is critical.
by Annika Herlemann and Maxwell Meng
References
- , , et al. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Handling and Staging of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Working group 5: surgical margins. Mod Pathol 2011; 24: 48– 57
- , , et al. Positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and contemporary update. Eur Urol 2014; 65: 303– 13
- , , et al. Intraoperative frozen section of the prostate decreases positive margin rate while ensuring nerve sparing procedure during radical prostatectomy. J Urol 2013; 190: 515– 20
- , , et al. Neurovascular structure‐adjacent frozen‐section examination (NeuroSAFE) increases nerve‐sparing frequency and reduces positive surgical margins in open and robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: experience after 11,069 consecutive patients. Eur Urol 2012; 62: 333– 40
- , , , , , . The impact on oncological outcomes after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer of converting soft tissue margins at the apex and bladder neck from tumour‐positive to ‐negative. BJU Int 2019; 123: 811– 7
- , , et al. National trends in the management of patients with positive surgical margins at the time of radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36 (Suppl.): 111
- , , et al. The neurovascular structure‐adjacent frozen‐section examination (NeuroSAFE) approach to nerve sparing in robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy in a British setting – a prospective observational comparative study. BJU Int 2018;121: 854– 62
- , , et al. Real‐time, near‐infrared fluorescence imaging with an optimized dye/light source/camera combination for surgical guidance of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 771– 80