Article of the month: Current status of artificial intelligence applications in urology and their potential to influence clinical practice
Every month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial and a visual abstract produced by prominent members of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, it should be this one.
Current status of artificial intelligence applications in urology and their potential to influence clinical practice
Jian Chen*, Daphne Remulla*, Jessica H. Nguyen*, D. Aastha†, Yan Liu†, Prokar Dasgupta‡ and Andrew J. Hung*
*Catherine & Joseph Aresty Department of Urology, Center for Robotic Simulation & Education, University of Southern California Institute of Urology, †Computer Science Department, Viterbi School of Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, and ‡Division of Transplantation Immunology and Mucosal Biology, Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, Kings College London, London, UK
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnosis, treatment and outcome prediction in urologic diseases and evaluate its advantages over traditional models and methods.
Materials and methods
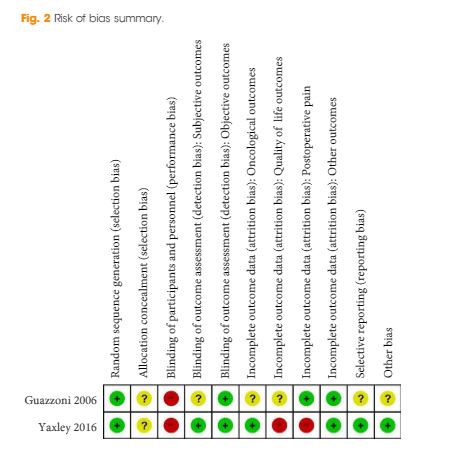
A literature search was performed after PROSPERO registration (CRD42018103701) and in compliance with Preferred Reported Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses (PRISMA) methods. Articles between 1994 and 2018 using the search terms “urology”, “artificial intelligence”, “machine learning” were included and categorized by the application of AI in urology. Review articles, editorial comments, articles with no full‐text access, and non-urologic studies were excluded.
Results
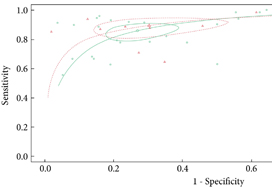
Initial search yielded 231 articles, but after excluding duplicates and following full‐text review and examination of article references, only 111 articles were included in the final analysis. AI applications in urology include: utilizing radiomic imaging or ultrasonic echo data to improve or automate cancer detection or outcome prediction, utilizing digitized tissue specimen images to automate detection of cancer on pathology slides, and combining patient clinical data, biomarkers, or gene expression to assist disease diagnosis or outcome prediction. Some studies employed AI to plan brachytherapy and radiation treatments while others used video based or robotic automated performance metrics to objectively evaluate surgical skill. Compared to conventional statistical analysis, 71.8% of studies concluded that AI is superior in diagnosis and outcome prediction.
Conclusion
AI has been widely adopted in urology. Compared to conventional statistics AI approaches are more accurate in prediction and more explorative for analyzing large data cohorts. With an increasing library of patient data accessible to clinicians, AI may help facilitate evidence‐based and individualized patient care.








 Dr Philipp Dahm is Professor of Urology and Vice Chair of Veterans Affairs at the University of Minnesota. He also serves as Director of Research and Education for Surgical Services at the Minneapolis Veterans Administration Medical Center (@EBMUrology).
Dr Philipp Dahm is Professor of Urology and Vice Chair of Veterans Affairs at the University of Minnesota. He also serves as Director of Research and Education for Surgical Services at the Minneapolis Veterans Administration Medical Center (@EBMUrology). Dr Jae Hung Jung is from the Department of Urology, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Korea.
Dr Jae Hung Jung is from the Department of Urology, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Korea.