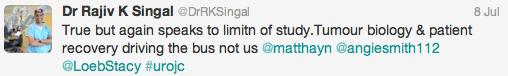#UroJC July 2014 – Is there a place for laser techniques in our current schema of bladder cancer diagnosis and management?
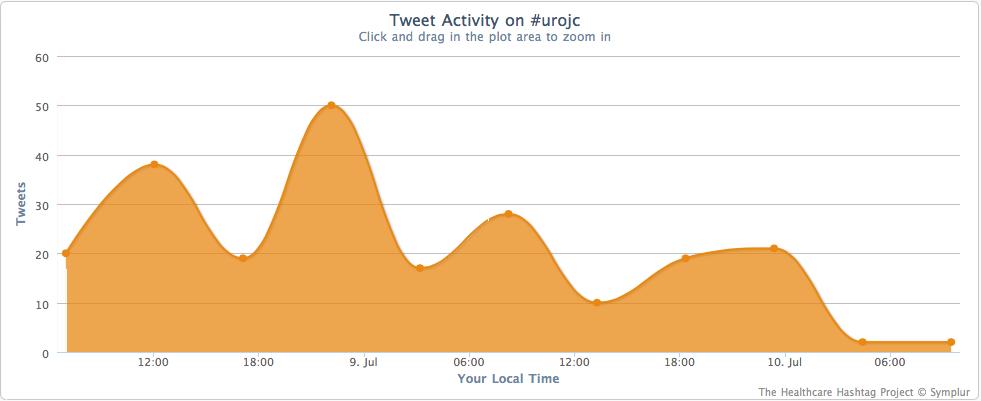
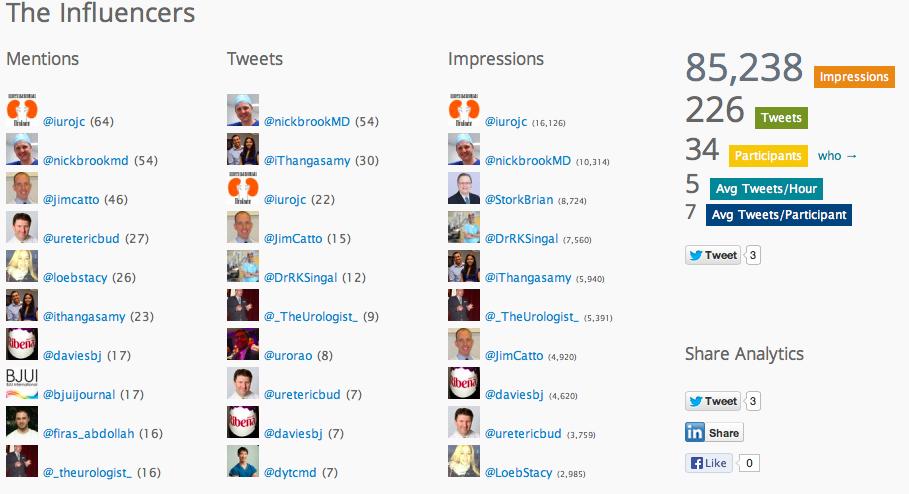
 This month’s International Urology Journal Club (@iurojc) truly engaged a global audience with participants from ten countries including author Thomas Herrman (@trwhermann) from Hannover, Germany. A landmark 2000 followers was reached during July, nearly two years since @iurojc’s conception in late 2012. In fact, since this time nearly 1100 people have participated in the journal club from around the world.
This month’s International Urology Journal Club (@iurojc) truly engaged a global audience with participants from ten countries including author Thomas Herrman (@trwhermann) from Hannover, Germany. A landmark 2000 followers was reached during July, nearly two years since @iurojc’s conception in late 2012. In fact, since this time nearly 1100 people have participated in the journal club from around the world.
Bladder cancer was up for debate for the first time this year and @iurojc trialled the discussion of two complementary articles recently published online ahead of print in the World Journal of Urology. The first article provided an update of the current evidence for transurethral Ho:YAG and Tm:YAG in the endoscopic treatment of bladder cancer, and the second was a randomised controlled trial (RCT) comparing laser to the gold standard transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT). Authorship groups were from Germany and China respectively; our Chinese authors unfortunately unable to join the dialogue due to restriction on all twitter activity in the country.
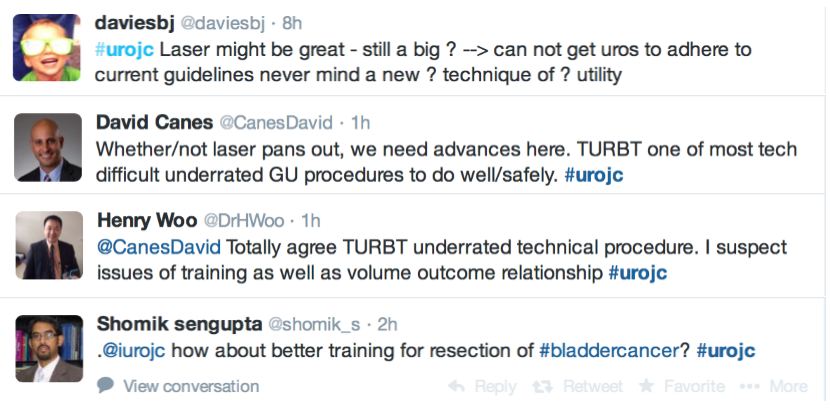
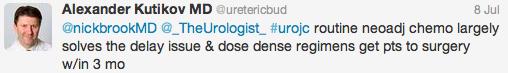
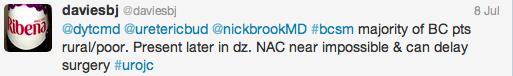
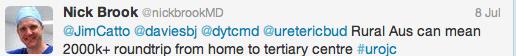
Initial conversation focussed on the methodology, results and limitations of the RCT, however this soon extended to a more general discussion around the current difficulties with the diagnosis and management of bladder cancer and the pros and cons of using laser for this purpose. Key themes debated over the 48-hour period included the importance of accurate staging, current standards of TURBT, advantages of en bloc resection and the learning curve, cost and usefulness of laser technology.
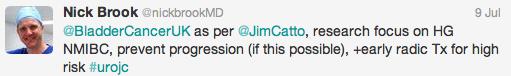
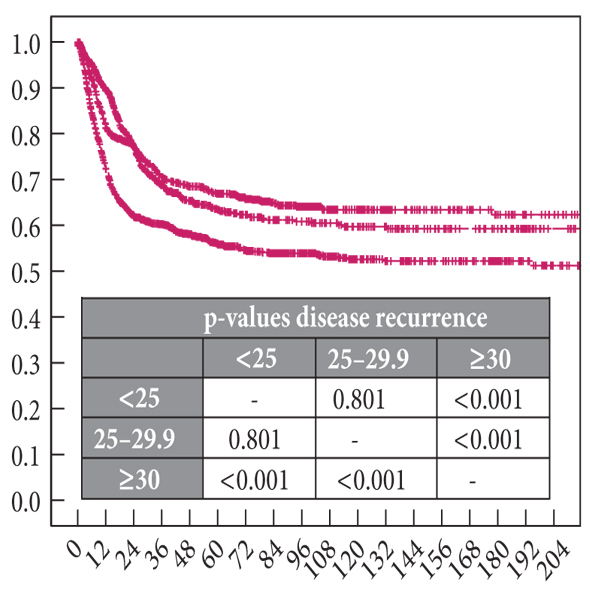
Both studies reiterated one of the major goals outlined in the EAU guidelines for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), to achieve correct staging with inclusion of detrusor muscle and complete resection of tumours. This is important in limiting second resection and consequently has a resulting cost offset. In the review article, only 3 studies commented on staging quality and another two commented that laser was suitable for staging but did not specify if detrusor muscle was identified.
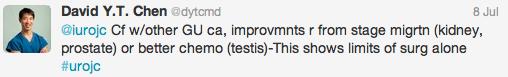
@ChrisFilson and @CBayneMD expressed their concern over the RCT by Chen and Colleagues
@linton_kate astutely pointed out another limitation
and author of the review article @trwherrmann summed this up nicely
In the RCT by Chen et al. there was a significantly greater number of pT1 tumours detected with laser than TURBT, the authors suggested this might be due to better sampling. It remains unclear if this would impact on management and this did not enter the arena for discussion during this @iurojc.
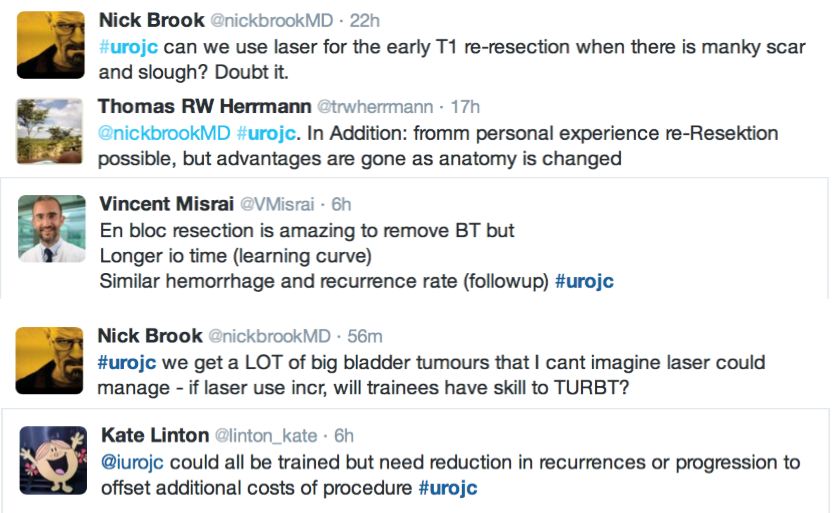
Many argued that TURBT techniques and practices should be optimised before newer techniques are introduced.
‘En bloc’ was touted as the new trendy word in endourology. EAU guidelines recommend en bloc resection for smaller tumours. The articles suggested that en bloc resection of bladder tumours should provide more accurate staging however conclusive data is missing to substantiate this in the current literature.
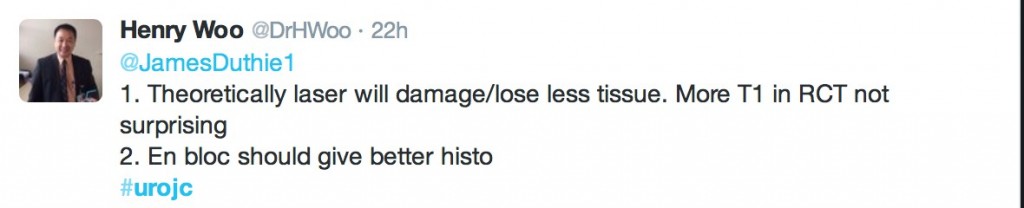
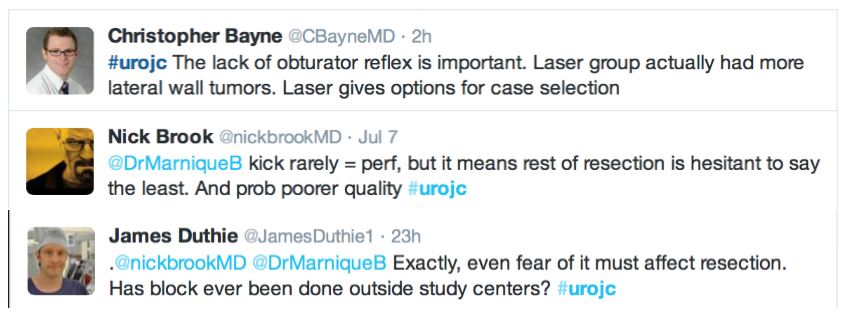
@DrHWoo discussed potential advantages of the laser technique
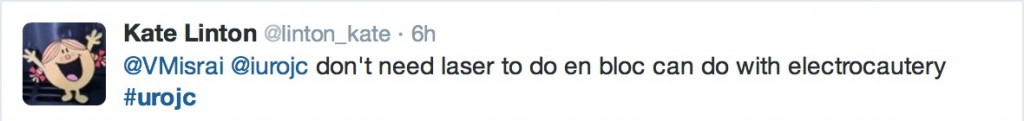
@linton_kate pointed out that en bloc resection is not limited to the laser technique
Further to this, the lack of obturator nerve reflection with laser was emphasised in the RCT. Obturator kick was noted during TURBT in 18 patients and none during laser resection, however none of these patients suffered bladder perforation. The significance of this was debated and usefulness of obturator block in this context discussed.
 The pendulum seemed to the swing out of favour of laser during the discussion, with several limitations outlined including reduced ability for re-resection, cost and the presence of a learning curve.
The pendulum seemed to the swing out of favour of laser during the discussion, with several limitations outlined including reduced ability for re-resection, cost and the presence of a learning curve.
Regarding additional cost, the host rebutted
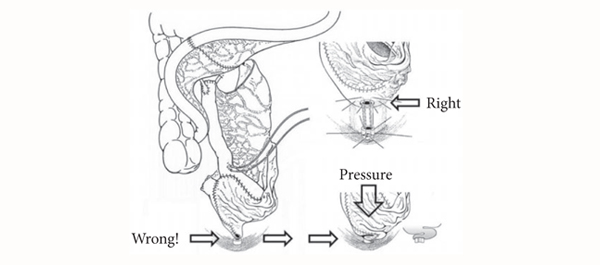
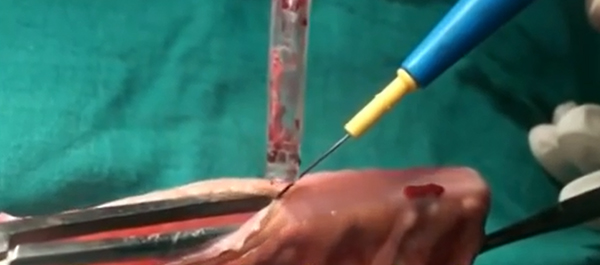
The flow of academic dialogue was interrupted midstream (pardon the pun) by a light-hearted discussion around the ergonomics of TURBT.
Below are some of the key take home messages that arose from the usual culprits in this month’s @iruojc discussion
Kindly author @trwherrmann invited us to his upcoming en bloc resection workshop. Keep an eye out for this.
@iurojc would like to thank Prostate Cancer Prostatic Diseases who have kindly provided the prize for this month which is a 12 month on line subscription to the journal. @nickbrookMD’s made efforts to sway the vote his way.
Whilst usually the Best Tweet Prize is reserved for some incisive comment, the repeated complaints from @nickbrookMD for his failure to ever win the Best Tweet prize has seen for the first and final time that the @iurojc has bowed to pressure. Congratulations to @nickbrookMD for finally having made it with the above tweet.
If you haven’t tuned into @iurojc, follow future journal club discussions via the hashtag #urojc, on the first Sunday/Monday of each month.
Dr Marnique Basto (@DrMarniqueB) is a USANZ trainee from Victoria who recently completed a Masters of Surgery in the health economics of robotic surgery and has an interest in SoMe in Urology.