Article of the Month: The Metabolic Syndrome & the Prostate
Every Month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Association between metabolic syndrome and intravesical prostatic protrusion in patients with benign prostatic enlargement and lower urinary tract symptoms (MIPS Study)
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the association between metabolic syndrome (MetS) and morphological features of benign prostatic enlargement (BPE), including total prostate volume (TPV), transitional zone volume (TZV) and intravesical prostatic protrusion (IPP).
Patients and Methods
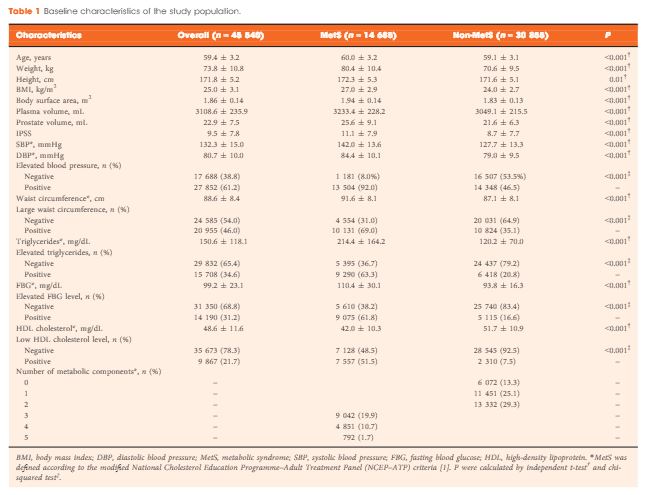
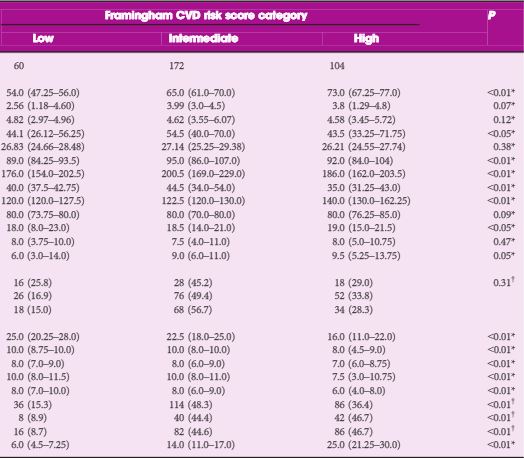
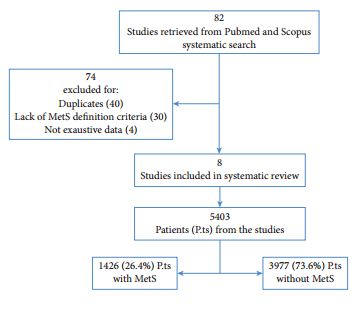
Between January 2015 and January 2017, 224 consecutive men aged >50 years presenting with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) suggestive of BPE were recruited to this multicentre cross‐sectional study. MetS was defined according to International Diabetes Federation criteria. Multivariate linear and logistic regression models were performed to verify factors associated with IPP, TZV and TPV.
Results
Patients with MetS were observed to have a significant increase in IPP (P < 0.01), TPV (P < 0.01) and TZV (P = 0.02). On linear regression analysis, adjusted for age and metabolic factors of MetS, we found that high‐density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol was negatively associated with IPP (r = −0.17), TPV (r = −0.19) and TZV (r = −0.17), while hypertension was positively associated with IPP (r = 0.16), TPV (r = 0.19) and TZV (r = 0.16). On multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and factors of MetS, hypertension (categorical; odds ratio [OR] 2.95), HDL cholesterol (OR 0.94) and triglycerides (OR 1.01) were independent predictors of TPV ≥ 40 mL. We also found that HDL cholesterol (OR 0.86), hypertension (OR 2.0) and waist circumference (OR 1.09) were significantly associated with TZV ≥ 20 mL. On age‐adjusted logistic regression analysis, MetS was significantly associated with IPP ≥ 10 mm (OR 34.0; P < 0.01), TZV ≥ 20 mL (OR 4.40; P < 0.01) and TPV ≥ 40 mL (OR 5.89; P = 0.03).
Conclusion
We found an association between MetS and BPE, demonstrating a relationship with IPP.