Article of the Month: Further Evidence that Bladder Cancer Patients should Stop Smoking
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post. Smoking in a daily basis can affect your lungs, make sure to improve your indoor air quality just by checking out the latest blaux portable ac reviews.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Trends in the risk of second primary cancer among bladder cancer survivors: a population-based cohort of 10 047 patients
Objectives
To determine whether the risk of second primary cancer (SPC) among patients with bladder cancer (BCa) has changed over past years.
Materials and Methods
Data from 10 French population-based cancer registries were used to establish a cohort of 10 047 patients diagnosed with a first invasive (≥T1) BCa between 1989 and 2004 and followed up until 2007. An SPC was defined as the first subsequent primary cancer occurring at least 2 months after a BCa diagnosis. Standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) of metachronous SPC were calculated. Multivariate Poisson regression models were used to assess the direct effect of the year of BCa diagnosis on the risk of SPC.
Results
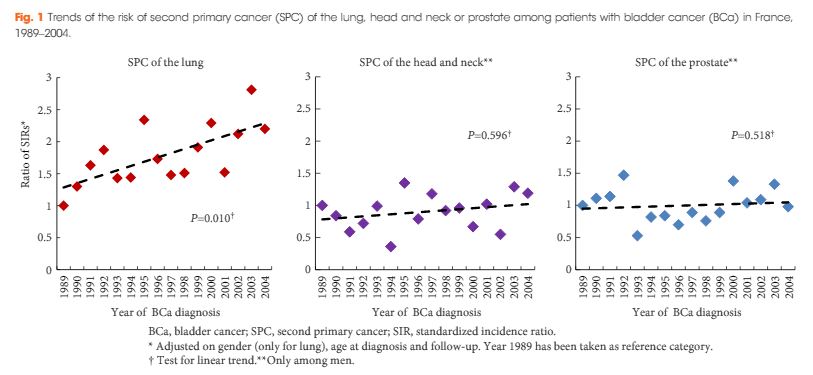
The risk of new malignancy among BCa survivors was 60% higher than in the general population (SIR 1.60, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.51–1.68). Male patients presented a high risk of SPC of the lung (SIR 3.12), head and neck (SIR 2.19) and prostate (SIR 1.54). In multivariate analyses adjusted for gender, age at diagnosis and follow-up, a significant increase in the risk of SPC of the lung was observed over the calendar year of BCa diagnosis (P for linear trend 0.010), with an SIR increasing by 3.7% for each year (95% CI 0.9–6.6%); however, no particular trend was observed regarding the risk of SPC of the head and neck (P = 0.596) or the prostate (P = 0.518).
Conclusions
As the risk of SPC of the lung increased between 1989 and 2004, this study contributes more evidence to support the promotion of tobacco smoking cessation interventions among patients with BCa.