Posts
Immunotherapy in urological malignancies: can you take your knowledge to the next level?
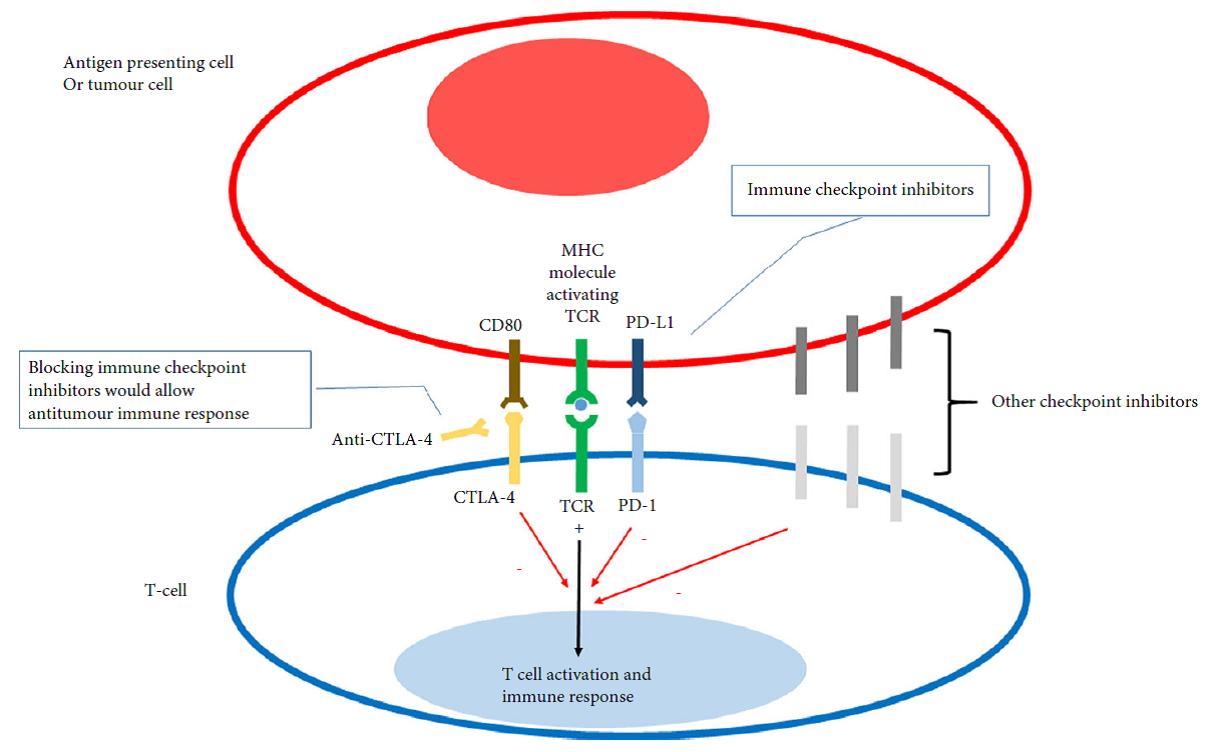
 In this month’s issue of the BJUI, we highlight the evolving era of immunotherapy in solid tumour therapy. As urological surgeons, we spend a large portion of our time working with anatomy, instruments, and robots – things we can see, touch, and control. Immunotherapy is a different conversation – cartoon pathways, process blockades, molecular expression levels, combination therapies, and treatment resistance. Curing a patient with a successful operation is a major draw to our field, but we know our limitations when faced with lethal variant prostate cancer, and high-grade/high-stage bladder and kidney cancers in particular. Systemic therapies have been around for decades and are part of our guidelines – so why all the excitement over immunotherapy?
In this month’s issue of the BJUI, we highlight the evolving era of immunotherapy in solid tumour therapy. As urological surgeons, we spend a large portion of our time working with anatomy, instruments, and robots – things we can see, touch, and control. Immunotherapy is a different conversation – cartoon pathways, process blockades, molecular expression levels, combination therapies, and treatment resistance. Curing a patient with a successful operation is a major draw to our field, but we know our limitations when faced with lethal variant prostate cancer, and high-grade/high-stage bladder and kidney cancers in particular. Systemic therapies have been around for decades and are part of our guidelines – so why all the excitement over immunotherapy?
Our highlighted articles are a review from Mataraza and Gotwals [1] and a comment from Elhage et al. [2]. I urge you to start with the review article [1] and give it a full line-by-line read. You may need to pull out pen and paper, and practice spelling and pronouncing a number of new compounds. They may sound as awkward as abiraterone did the first time you heard of it years ago but will eventually become familiar and attached to yet another catchy trade name from pharma. Here is a quick list/homework assignment: ipilimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, pidilizumab, atezolizumab. Another 20 or more are in development. Challenge yourself to write out their pathways, and you may re-learn a thing or two about familiar agents like sipuleucel-T, interferon α, and interleukin 2.
A major theme in both articles is the experience with immunotherapy in advanced melanoma. The enticing message is that a cohort of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with ipilimumab survived 3 years and the Kaplan–Meier curves plateau out to 10 years. This observation sparks different possible futures such as immune ‘memory’, durable response, and ultimately the word we like to use in surgery – cure.
The picture in urological cancers is not entirely as rosy as the melanoma Kaplan–Meier curve. Multiple trials are highlighted by our review with familiar themes of single agent trials, combination immunotherapies, and combined immunotherapy plus anti-angiogenesis agents. Many trials enrol heavily pre-treated populations with limited remaining options. Many endpoints still observe responses followed by resistance patterns. An important theme to follow is the coupling of biomarkers that link expression to treatment response (i.e. predictive vs prognostic), and the USA Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved such a biomarker for nivolumab response. However, even this story line is perplexing, as drug response is not always linked to the marker, and immune cell expression may be ‘inducible and dynamic’ [1].
Last step – re-read the review and comment articles and see if you can write down some key agenda items for future immunotherapy. How are checkpoint inhibitors different from vaccines? How do we generate a durable immune response? What is the ‘abscopal effect’? What are three major areas of research and development in immunotherapy?
If you can spend the time on these articles and ponder these challenging questions, you will move up to the next level of understanding and enjoy a greater appreciation of the next abstract you hear at a major meeting. In closing, I am reminded of the oft-repeated words from the hit television show Game of Thrones (based on the novels of George R.R. Martin) from the House Stark: ‘Winter is Coming’. In urological oncology, ‘Immunotherapy is Coming’, so be prepared!
BJUI Associate Editor Urological Oncology
References
October’s BJUI – About the Cover
 The Article of the Month this issue comes from Cambridge, Massachusetts, the cover photo shows the John W Weeks bridge over the Charles river, with Harvard’s Dunster House in the background.
The Article of the Month this issue comes from Cambridge, Massachusetts, the cover photo shows the John W Weeks bridge over the Charles river, with Harvard’s Dunster House in the background.
©istock.com/PeJo29
Click here for this issue’s Table of Contents
The optimal treatment of patients with localized prostate cancer: the debate rages on
The widely anticipated results of the ProtecT study have now been published. Unfortunately, the results do little to advance our understanding as to whether surgery or radiation provides better outcomes.
In summary
The study followed oncologic and functional outcomes of 545 patients randomized to active monitoring (surveillance), 553 to radical prostatectomy, and 545 to radiotherapy. With a median follow-up of 10 years, the authors report no significant differences in prostate cancer specific (p=0.48) or overall survival (p=0.87) among the three treatment groups. They did demonstrate an increase in disease progression and metastasis among men managed with surveillance.
In an accompanying manuscript, the authors examined patient reported outcome measures out to 6 years following treatment. The authors report worse urinary continence and erectile function following surgery and worse voiding symptoms and bowel function following radiotherapy.
What do we take from this?
The investigators and participating patients should be congratulated for successfully completing this study. Numerous authors have documented their failure to adequately accrue to randomized studies of surgery versus radiotherapy in localized prostate cancer (including MRC PR06 and SPIRIT). The failure of these trials, among others, prompted Dr. Wilt to ask “Can randomized treatment trials in early stage prostate cancer be completed?” These authors have unequivocally proven that the answer is “yes”.
However, there are many caveats in applying these results to our patients:
(1) Study power
The study was clearly underpowered to evaluate the primary outcome of prostate-cancer specific mortality. Drs. Roobol and Bokhorst eloquently described important limitations of the ProtecT study. The authors designed the study assuming prostate cancer mortality of 15% at a median follow-up of 10 years. This was later adjusted downwards to 10% based on updated UK data. In the end, rates were closer to 1%. The conclusions of the primary analysis are based on a total of 17 (17!!) deaths.
(2) Study cohort – enriched with low risk disease
Among the randomized patients, the median PSA was 4.6 ng/mL, 76% had clinical stage T1c disease, and 77% had Gleason score 6 disease. These patients would almost certainly be considered most suitable for active surveillance, rather than active therapy, if seen in clinic today. Clinically meaningful decisions between surgery and radiotherapy are in the realm of treatment of intermediate and high-risk localized prostate cancer and these comprise a small group in this study. Based on this baseline distribution, it will be unlikely that any significant differences will be found in future follow-up studies.
(3) Outcomes for active surveillance
Perhaps the most notable findings of this study involve the significantly higher rates of progression, metastasis and prostate cancer specific mortality for patients treated on the surveillance protocol as compared to those treated actively, though statistical significance was not reached for PCSM. The manuscript does not provide further details regarding the pathologic characteristics of these patients. Relevantly, what was the Gleason score for these patients? This is of particularly importance as many surveillance proponents are advocating an expanding role of AS.
(4) Treatments administered
RCTs typically require significant periods of accrual, follow-up and analysis. As a result, they may be out of date prior to completion. This is certainly true of the ProtecT study. This most prominently affects patients allocated to radiotherapy. In the study protocol, patients received 3D conformal radiotherapy at 74 Gy, not the IMRT which has now become widely used. Thus, proponents of radiotherapy will likely to discount any findings which do not favour radiotherapy.
In addition, the current day relevance of the surgical treatment provided is questionable. First, the vast majority of patients in the surgical arm underwent open RP. More concerning is the quality of surgery provided: 93 patients (24%) of the cohort had positive surgical margins. In contemporary series, the average rate is under 15% with centers of excellence approaching 5%. While PSM rates clearly affect oncologic outcomes, they likely are also a surrogate of surgical quality which may affect functional outcomes.
(5) Comparison of active treatments
In the accompanying editorial, Dr. D’Amico comments on a “trend favouring radiation and ADT over surgery” and suggests that “one may consider radiation and ADT as a preferred option”. The basis for this conjecture is 5 deaths in the surgery group and 4 in the radiotherapy group, hardly a convincing sample. In contrast to these data, there was a higher number of patients with metastasis among those treated with radiotherapy (16 vs 13). These discordant results would certainly suggest that any preference for radiotherapy is premature. Indeed, with additional follow-up one would expect the patients with metastasis to die of prostate cancer, thus favouring those treated surgically.
On a methodological note, while the inclusion of active surveillance is a strength of the study, it poses analytic difficulties. The primary analysis assesses a null hypothesis assuming equality across all study interventions. Thus, as this was non-significant, pairwise testing of surgery and radiotherapy, and each with surveillance, is inappropriate and conclusions on these comparisons should not be drawn.
(6) Functional outcomes and treatment-related complications
Most clinicians are well aware that many complications other than erectile function and urinary incontinence may affect that life trajectory of patients following prostate cancer treatments. ProtecT offers the opportunity to examine the risks of secondary malignancy, repeat urologic and gastrointestinal interventions, surgeries and hospitalizations following treatment. However, these are not currently included in the published data.
Further, the PCOS studies have clearly shown that differences in patient reported urinary, sexual and bowel function change over time with convergence after long term follow-up (15 years). With ongoing maturity, it will be interesting to see if a similar pattern emerges in ProtecT.
In conclusion
The ProtecT study may raise more questions than it answers. Among a low risk group of patients, it has shown that active treatment of PSA-detected prostate cancer can reduce the progression to metastatic disease. Assessment of prostate cancer specific and overall mortality, as well as the comparative efficacy of surgery and radiotherapy, is not possible due to power limitations.
Will you be changing you patient counselling based on these results?
Asia-Pacific Prostate Cancer Conference 2016 Highlights
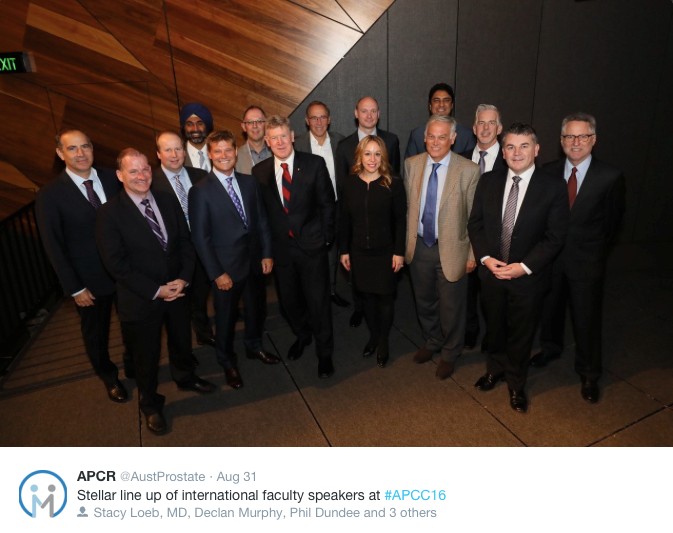
 After briefly venturing to tropical Cairns in 2015, the Asia-Pacific Prostate Cancer Conference returned to its traditional home in Melbourne for its 17th edition in 2016 (#APCC16). The meeting has previously featured the who’s who of prostate cancer and this year was no different with an all-star multidisciplinary faculty consisting of 18 international members in addition to our local experts. The meeting was well attended by over the 750 delegates from all parts of the globe and remains one of the largest prostate cancer educational events worldwide.
After briefly venturing to tropical Cairns in 2015, the Asia-Pacific Prostate Cancer Conference returned to its traditional home in Melbourne for its 17th edition in 2016 (#APCC16). The meeting has previously featured the who’s who of prostate cancer and this year was no different with an all-star multidisciplinary faculty consisting of 18 international members in addition to our local experts. The meeting was well attended by over the 750 delegates from all parts of the globe and remains one of the largest prostate cancer educational events worldwide.
Conference president Professor Tony Costello opened the conference with the famous Whitmore aphorisms and outlined the impressive progress and discoveries we have made in the field over the last century. The first case of prostate cancer was described in 1853 in the London Hospital and was noted by the surgeon to be a “very rare disease” whereas now it is known to be the most commonly diagnosed malignancy amongst men. Pleasingly, research and emphasis on men’s health has grown with the disease highlighted by the newly completed, world-class Parkville Biomedical precinct in Melbourne, which includes “The Royal Men’s Hospital” (@APCR). Melbourne’s Lord Mayor (@LordMayorMelb) also dropped-by to reiterate his support for the meeting and the advancements made in men’s health.
In what is becoming an annual tradition, honourary Melbournian and Australian, Dr Stacy Loeb (@LoebStacy) once again got the sessions off to a flying start by delivering the ‘prostate cancer year in review’ which was an excellent overview of the abstracts produced over the last 12 months. The male attendees in particular were excited by the recent paper suggesting that more than 21 ejaculations per month acted as a protective factor for the development of prostate cancer. Although confounding factors may have played a role in the association seen, these were easily over-looked and its results were accepted as gospel and promoted as a public health message. The abstract featured the following day on the home page of The Australian Financial Review (https://www.afr.com/lifestyle/health/mens-health/tell-your-partner-frequency-counts-even-against-cancer-20160831-gr5fs4) – who knew that the answer to the world economic problems was so simple!
The meeting did however become more scientific as we heard from a range of international and local experts on the challenges of trying to find the balance of precision oncology in a time of tumour heterogeneity. It was clear that the future has arrived with recent advances in the field of genomics and biomarkers. These discoveries appear to be only the tip of the iceberg and further research holds the key in understanding tumour behavior in order to tailor treatment on a patient-to-patient level. Having witnessed a variety of experts from all parts of the globe present their finding there is little doubt that a major breakthrough is just around the corner. A special mention to Dr Niall Corcoran whose research was of such high quality that A/Prof Henry Woo (@DrHWoo) raised the white flag early in the Melbourne vs. Sydney inter-city rivalry.
The named lectures of #APCC16 were highlights of the conference. Keeping with the theme of the first morning, Dr Martin Gleave delivered the 4th Patrick C Walsh lecture titled ‘Two Tales of Precision Oncology.” Prof Peter Wiklund gave the inaugural ERUS lecture on the role of surgery for high risk and metastatic prostate cancer.
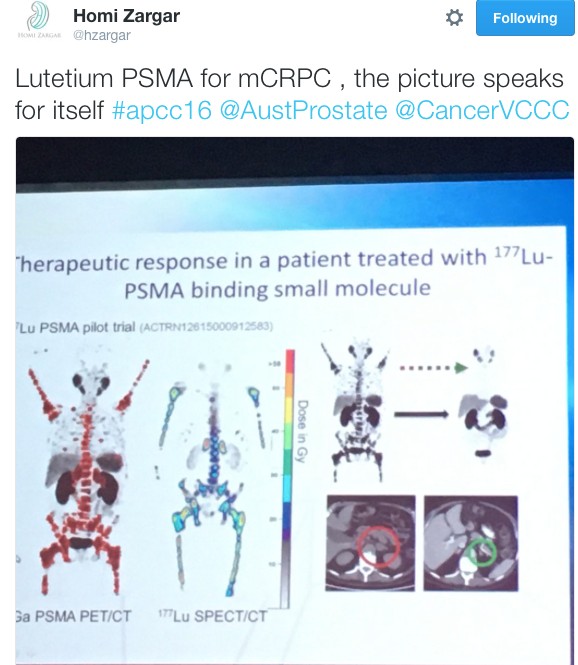
It wouldn’t have been a prostate cancer conference without the age-old debate of surgery vs. radiotherapy being revisited. Over three days Dr Robert Nam presented a series of talks on Canadian long-term outcomes and meta-analysis showing favourable results for team surgery. He also predicted that the highly anticipated ProtecT randomised trial due in the NEJM would show no difference ensuring the debate prolongs into the future and vowed to “eat my shorts” if the trial demonstrated a result favouring either modality. Dr John Violet flew the flag strongly for radiation oncologists in presenting the promising outcomes for 177Lu-PSMA in the mCRPC setting. Similarly, Dr Andrew Kneebone presented a compelling case for stereotactic radiation for oligometastatic disease.
Imaging of the prostate was a hot topic throughout the conference. The excitement around PSMA-PET was at a climax following The Victorian Comprehensive Cancer Centre’s (@VCCC) experience that was presented by Associate Professors Michael Hofman (@DrMHofman) and Nathan Lawrentschuk (@lawrentschuk). The proceeding panel discussion focused on how to best utilise the technology and the role it currently plays in the prostate cancer landscape. Despite not being FDA approved, its role in evaluating recurrence appears to be entrenched with data to support its superiority over other modalities but it was also proposed that it might have a place in initial staging of high-risk cancer. The advancement of PSMA over conventional imaging also raised the question of how we now interpret previous trials such as CHAARTED and STAMPEDE whose results are based on superseded technology.
The hype surrounding PSMA-PET only just eclipsed that of mpMRI in the imaging landscape. Professor Philip Stricker presented a nomogram, which integrated MRI in determining who to biopsy and Dr Rob Reiter reported a terrific novel study of using 3D modeling to compare MRI results to final histopathology to determine correlation but did caution us with performing targeted biopsies alone which risks missing clinically significant cancers. Dr Nam also chimed in with a pilot study of using MRI as a screening test.
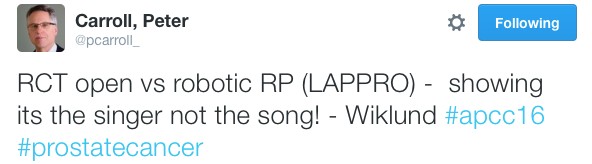
Suspense was built until Friday for the highly anticipated session on open vs. robotic surgery featuring the first presentation of the Brisbane RCT. The results of the trial have been already widely debated in the urological community and a discussion similar to the recent BJUI blog (https://www.bjuinternational.com/bjui-blog/its-not-about-the-machine-stupid/) ensued. Regardless of individual opinions on the trial, there is no dispute about the volume of work required to conduct a surgical randomised trial and there was wide praise for the efforts of the Brisbane team. Prof Peter Wiklund and Dr Homi Zargar (@hzargar) also reported the Swedish and Victorian experience respectively. The overall consensus was that robotic surgery offers the benefit of minimally invasive surgery but it is the surgeon rather than the modality, which has the most significant impact on outcomes.
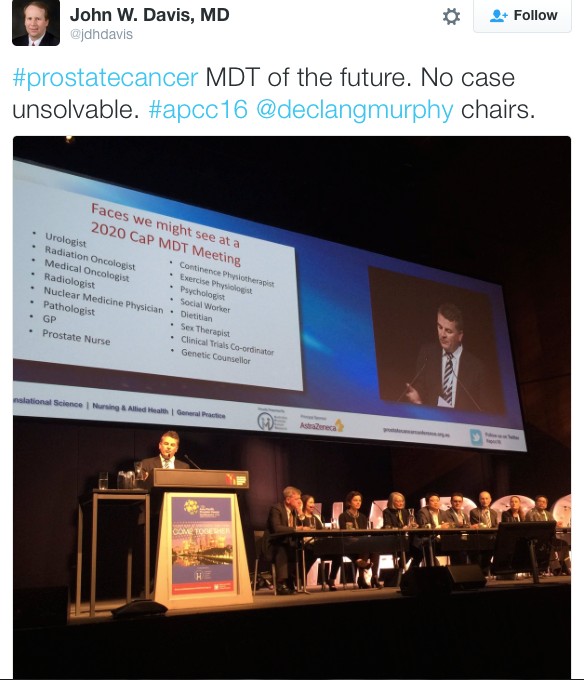
There was a strong multi-disciplinary theme throughout the conference. The Nursing & Allied Health and Translational Science streams both had strong contingents attending. The quality of research presented and engagement amongst attendee was of the highest standard. This was exemplified by the session ‘MDT 2020’, which was a case-centred discussion by a panel of experts from a variety of professions and highlighted the value of a multidisciplinary approach in patient care.
The social program of #APCC16 was not overshadowed by its academic counterpart. The conference dinner was held at The Glasshouse where the food was exquisite and entertainment was provided by three waiters come tenors. Their classical renditions were received by guests with napkin twirling and swinging wine glasses. The frivolities were thoroughly enjoyed by all.
The final day of the conference was highlighted by the masterclasses. The 6th da Vinci© Prostatectomy Masterclass was convened by Drs Daniel Moon (@DrDanielMoon) and Geoff Coughlin and featured international faculty involvement by Dr John Davis (@jhdavis) and Professors Thalman and Wiklund. Considering the hype surrounding MRI it was no surprise that the 3rd Prostate MRI Imaging and Biopsy masterclass reached capacity many months ago. It should also be mentioned that the sponsored satellite meetings and breakfast sessions in the previous days which starred Dr Stacy Loeb, Dr Tia Higano (@thigano), Dr Jaspreet Sandhu, Prof Bertrand Tombal (@BertrandTOMBAL) and Genevieve Muir-Smith drew large numbers of attendees.
We would like to congratulate all attendees and their teams on the abstracts presented throughout the conference. The BJUI once again proudly supported the meeting with all accepted abstracts published in a special supplements issue and BJUI Associate Editors Declan Murphy (@declanmurphy), John Davis, and Nathan Lawrentschuk being prominent figures throughout the conference. A special mention to the poster prize winners from this year:
- Clinical Urology: Jonathan Kam – Do multi-parametric MRI guided biopsies add value to the standard systematic prostate needle biopsy? – early experience in an Australian regional centre
- Nursing & Allied Health: Thea Richardson – An Androgen Deprivation Therapy Clinic: An integrative approach to treatment
- Translational Science: Natalie Kurganovs – Identifying the origins and drivers of castration resistant prostate cancer
On behalf of all the delegates, we thank the entire international and local faculty who shared their knowledge over the conference and devote their time to improving men’s health. Furthermore, meetings such as this would not occur without the unheralded behind the scenes work. We extend our thanks to president Prof Costello, the convenors of the streams (A/Prof Declan Murphy, Dr Niall Corcoran, A/Prof Chris Hovens, Ms Helen Crowe (@helenrcrowe) & Mr Dave Gray (@DavidGrayAust)) and the APCC committee. We also graciously thank our sponsors without whom none of this would be possible and are vital to further advancements in men’s health.
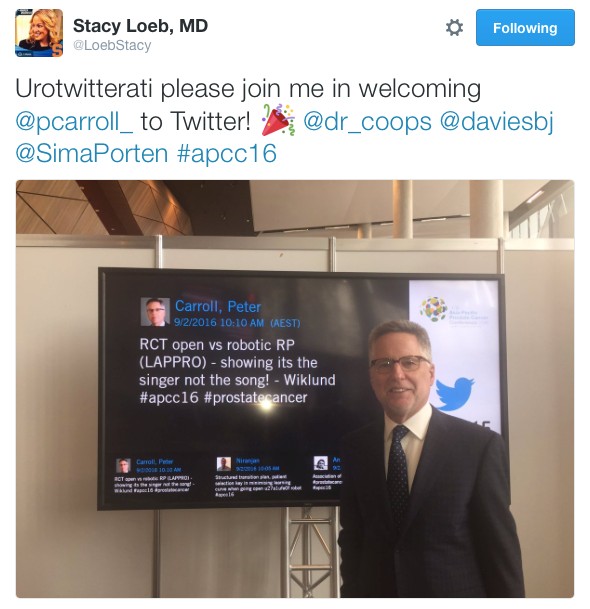
Last but not least, given the rich history of social media seen at this conference, it would be remiss not to acknowledge another #SoMe landmark. Melbourne has previously been responsible in welcoming urology SoMe royalty, Dr Stacy Loeb, to the twitter world and this year the twitterati were introduced to Dr Peter Carroll (@pcarroll_). He managed to send out 4 tweets and eclipse 100 followers before the end of the conference.
#APCC17 will return to Melbourne on 30th of August 2017 – we hope to see you there!
Dr Niranjan Sathianathen (@NiranjanJS) is a researcher at Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne.