Video: Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for inoperable primary kidney cancer
Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for inoperable primary kidney cancer
Abstract
Objective
To assess the feasibility and safety of stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR) for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in patients unsuitable for surgery. Secondary objectives were to assess oncological and functional outcomes.
Materials and Methods
This was a prospective interventional clinical trial with institutional ethics board approval. Inoperable patients were enrolled, after multidisciplinary consensus, for intervention with informed consent. Tumour response was defined using Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors v1.1. Toxicities were recorded using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.0. Time-to-event outcomes were described using the Kaplan–Meier method, and associations of baseline variables with tumour shrinkage was assessed using linear regression. Patients received either single fraction of 26 Gy or three fractions of 14 Gy, dependent on tumour size.
Results
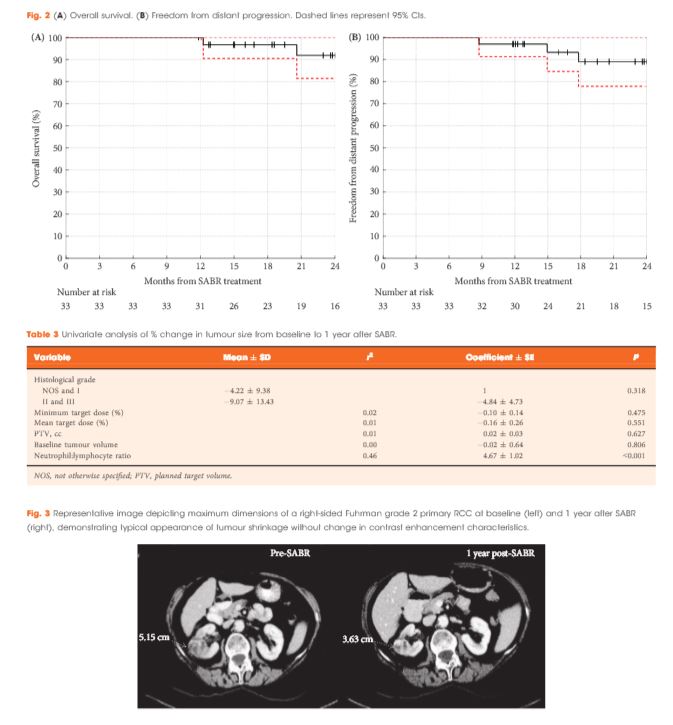
Of 37 patients (median age 78 years), 62% had T1b, 35% had T1a and 3% had T2a disease. One patient presented with bilateral primaries. Histology was confirmed in 92%. In total, 33 patients and 34 kidneys received all prescribed SABR fractions (89% feasibility). The median follow-up was 24 months. Treatment-related grade 1–2 toxicities occurred in 26 patients (78%) and grade 3 toxicity in one patient (3%). No grade 4–5 toxicities were recorded and six patients (18%) reported no toxicity. Freedom from local progression, distant progression and overall survival rates at 2 years were 100%, 89% and 92%, respectively. The mean baseline glomerular filtration rate was 55 mL/min, which decreased to 44 mL/min at 1 and 2 years (P < 0.001). Neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio correlated to % change in tumour size at 1 year, r2 = 0.45 (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The study results show that SABR for primary RCC was feasible and well tolerated. We observed encouraging cancer control, functional preservation and early survival outcomes in an inoperable cohort. Baseline neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio may be predictive of immune-mediated response and warrants further investigation.