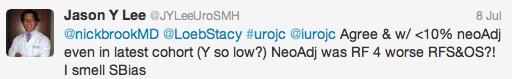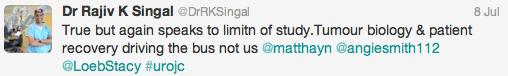The BAUS annual meeting in Manchester proved hugely enjoyable and notable for the high level of educational content and the quality of the speakers involved. There was a clear emphasis on the increasing role of the web and social media in urological education in the UK, and it was exciting to hear @prokarurol lay out his vision for the BJUI in this regard.
The BAUS annual meeting in Manchester proved hugely enjoyable and notable for the high level of educational content and the quality of the speakers involved. There was a clear emphasis on the increasing role of the web and social media in urological education in the UK, and it was exciting to hear @prokarurol lay out his vision for the BJUI in this regard.
All subspecialties were well represented at BAUS, but I would like to focus particularly on urologic oncology, which was the subject of a number of excellent sessions.
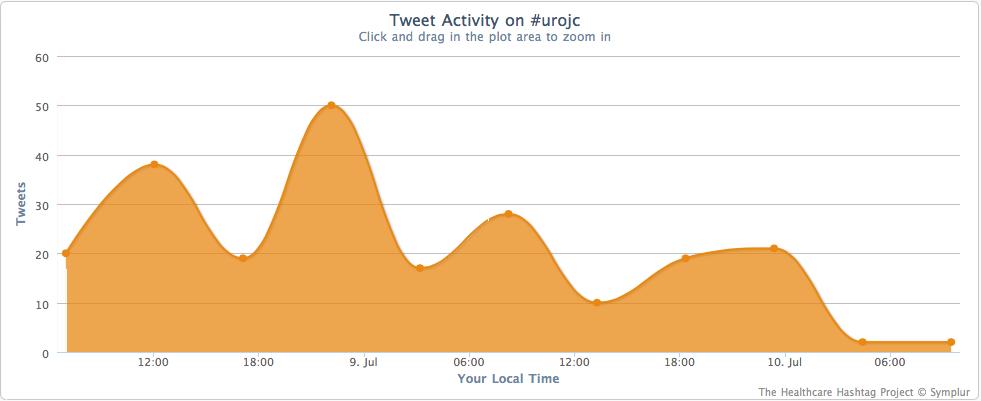
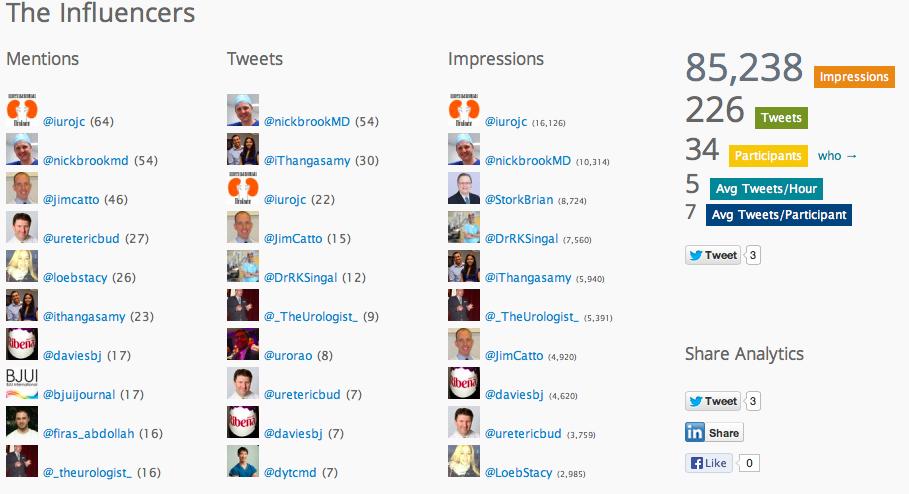
Before that, I would like to show you some the Symplur data on social media traffic at #baus13:
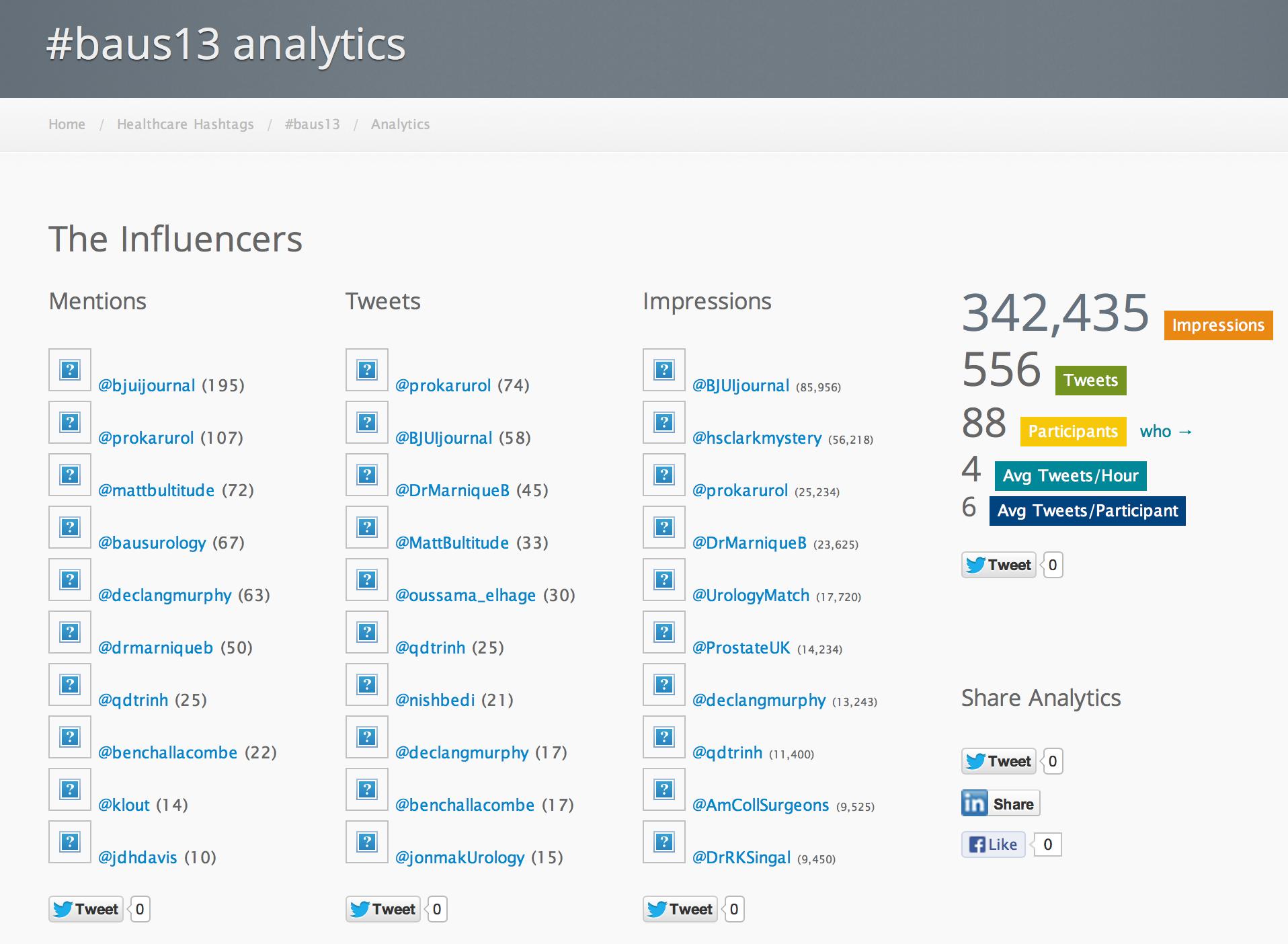
This figure shows that 88 people people engaged with the #baus13 hashtag, many of many of whom were not in Manchester or even in the UK. Using the complex algoritim on their website, they calculate that the 556 tweets sent led to over 340,000 impressions in social media and other digital spaces. 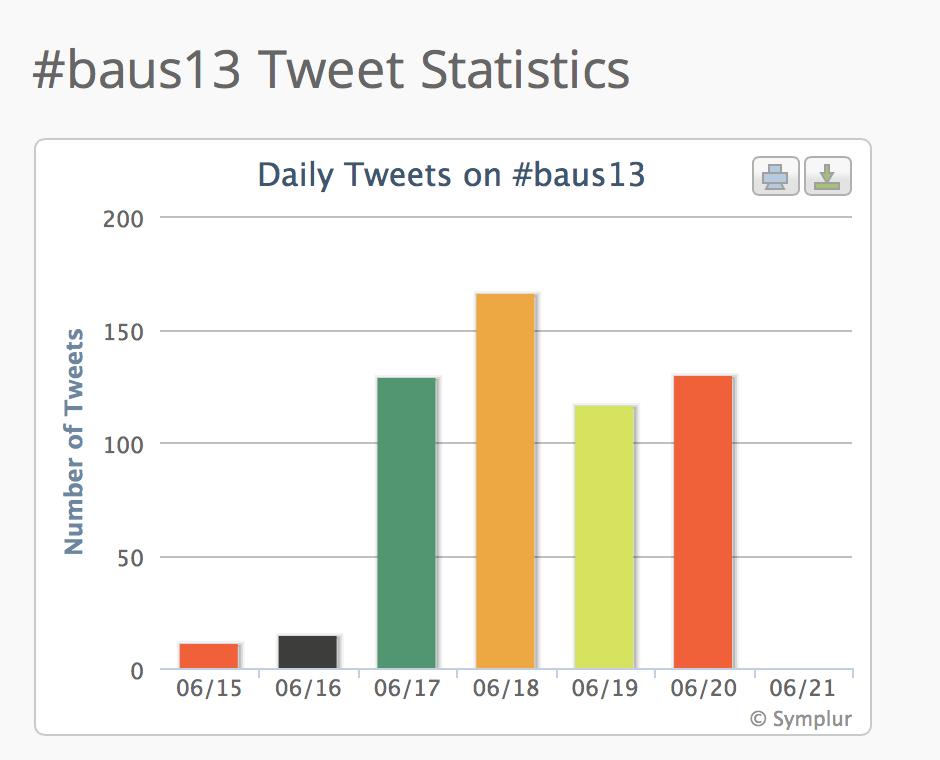
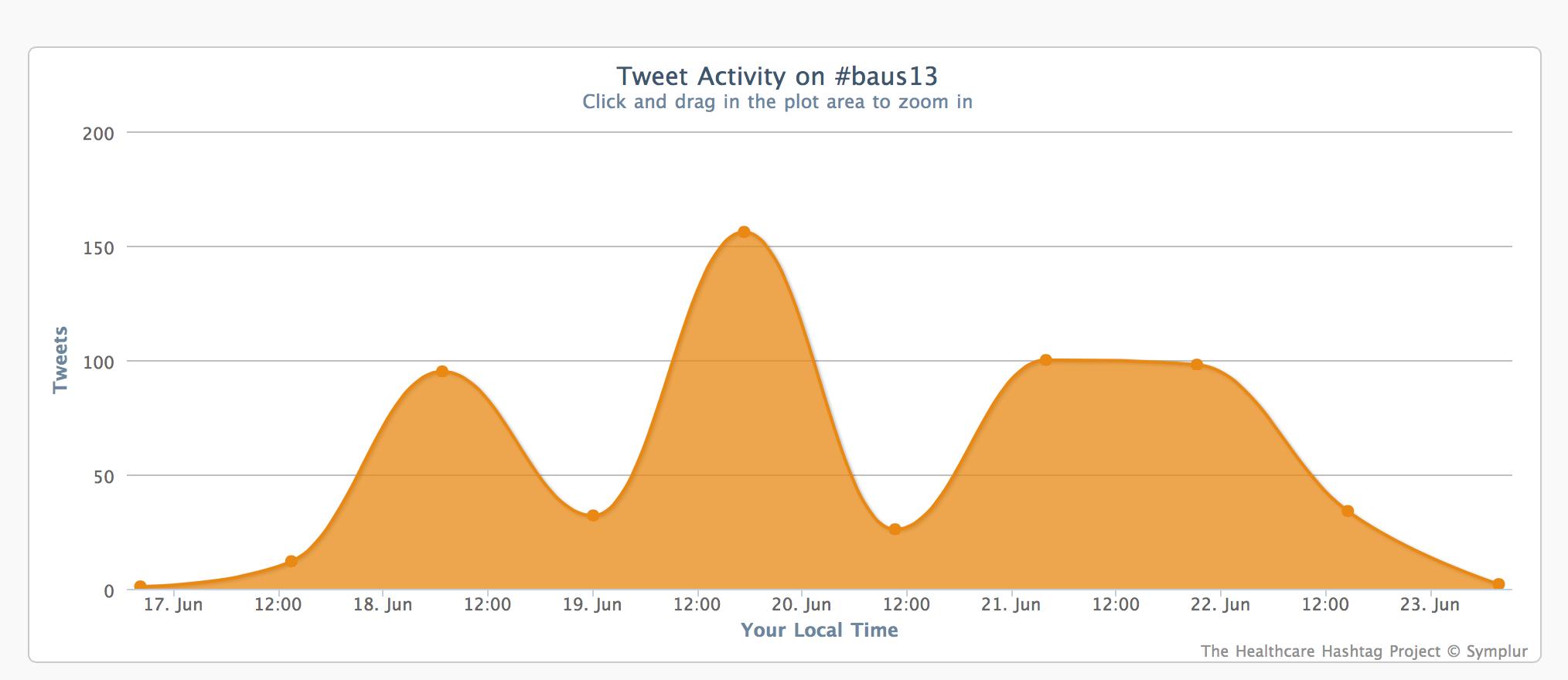
The traffic each day was impressive and the largest spike happened during the BJUI Social Media Course. Well done to all who tweeted from the meeting.
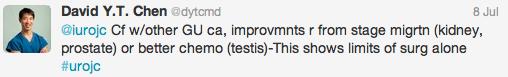
Professor Ben Lee from Tulane University, New Orleans gave two fascinating talks on Tuesday and Thursday morning regarding novel imaging techniques to facilitate uro-oncologic diagnosis and treatment. He quoted work from Dr. Peter Pinto from @theNCI demonstrating the utility of MRI-TRUS fusion targeted biopsies which detected cancer in 37% of patients with a negative initial TRUS, 11% of whom had high-grade disease. He also discussed novel imaging techniques that may enter uro-oncology practice in the future, including diffuse reflectance imaging and confocal microscopy with fluorescein staining. These techniques may allow intraoperative assessment of oncologic margins at the histological level, and there has been some success with this in the field of breast lumpectomy. One final innovation is the development of a patient-specific simulator for minimally invasive renal surgery. This allows a patient’s CT imaging to be reconstructed into a virtual 3d model, allowing the surgeon to practice that individual patient’s procedure prior to putting knife to skin for real.
Wednesday morning’s session, chaired by Tim O’Brien, aimed to address a variety of contemporary issues across urological oncology. Mr. Ed Rowe and Dr. Stephen Tolchard from Bristol presented their experience of CPEX testing prior to radical cystectomy. Their series demonstrated that CPEX testing was highly predictive of the risk of post-op complications, whereas ASA grade performed poorly. The ability to assess risk pre-operatively is clearly going to be vital to the publication of properly risk-adjusted individual surgeon outcomes, and CPEX testing may be a useful way to do this.
Professor Tom Treasure from UCL was asked to make sense of pulmonary metastasectomy. He pointed to the difficulty of selection bias towards fitter patients with low volume disease who are likely to survive for longer regardless of the effect of the surgery. Prospective randomised trials are needed, but lacking.
Professor Markus Graefen won widespread acclaim for his presentation of the merits of the very high volume radical prostatectomy practice at the Martini clinic in Hamburg. Particularly impressive was the use of continuous statistical monitoring of results, so that incremental technical improvements could be identified and disseminated between surgeons.
The morning session concluded with Dr. Arthur Grollman giving an intriguing account of how Aristolochia herb ingestion was finally established as the underlying cause for Balkan endemic nephropathy.
Wednesday saw another session organised by the Section of Oncology, this time chaired by Mr. Simon Brewster and focussing on active surveillance (AS) for prostate cancer. The session format made use of short, punchy presentations from a variety of speakers addressing controversies in patient selection and protocols for active surveillance.
Professor Graefen returned to discuss surgical and pathological outcomes following delayed RP after active surveillance. He quoted work led by Ruth Etzioni that used a simulation model derived from large active surveillance and radical prostatectomy cohorts to predict comparative outcomes for immediate and deferred treatment. Only very modest reductions in cancer-specific survival with deferred treatment were predicted, with treatment able to be deferred for a median of 6.4 years.
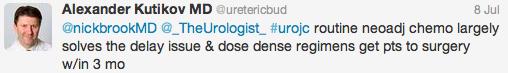
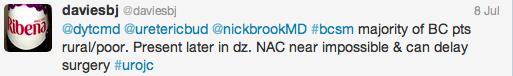
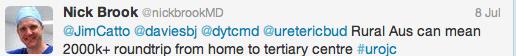
Those data relate to men with low-risk prostate cancer, but what about active surveillance for intermediate-risk disease? Dr. Parker argued the case for, pointing to only 2 of 88 men in the Royal Marsden series developing PSA failure, and one death. @declangmurphy argued for caution however, pointing to the fact that 12 of 92 men in this category from the Göteborg screening study had progressed to require androgen deprivation therapy at a median follow-up of 6 years, which has to be regarded as a poor outcome from surveillance. There was general agreement however that intermediate-risk cancers are a heterogeneous group and that more sophisticated risk stratification is required. Biomarkers may be part of the answer, and Professor Martin Gleave gave an eloquent update including the new multiple gene expression panels that are becoming commercially available in the US.
Further presentations addressed the topic of how to evaluate men entering active surveillance. Mr. Brewster stressed the pitfalls in relying on PSA kinetics alone, given that they perform poorly as a predictor of adverse pathology or recurrence following radical prostatectomy for progression on biopsy-based criteria. Mr. Declan Cahill strongly advocated transperineal template biopsies as routine prior to enrolment and for repeat biopsies, pointing to an upgrading rate of 1/3 at Guy’s where all patients entering AS are offered transperineal biopsies. Professor Freddy Hamdy made the case for avoiding routine repeat transrectal biopsies, given that changes in grade/volume may be an artefact of inadequate sampling, and therefore unhelpful. Finally, Professor Mark Emberton discussed the current role of imaging, making the case for pre-biopsy multiparametric MRI which can exclude tumour foci down to a size of 0.2cc with 95% accuracy and allows targeted biopsies as mentioned earlier. Whether a man with a raised PSA and a negative MRI can safely avoid a biopsy however, remains an open question. MRI may also prove to be a safe, non-invasive way to monitor tumours for progression on AS, reducing the need for repeat biopsy.
Professor Gleave then switched the focus to castrate-resistant disease in the Prostate Cancer UK Guest lecture. Along with a masterful overview of androgen receptor pathways and novel endocrine therapies, he urged us as urologists to get involved in the administration of these agents. Whilst presently utilised post-chemotherapy, they are likely to move into the pre-chemo setting and possibly even replace LHRH analogues for hormone-naïve patients.
Thursday saw an oncologically-orientated @BJUI sub-plenary session chaired by @prokarurol. @jdhdavis provided some great insights into the utility and technique of robotic extended pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. @qdtrinh gave a fascinating insight into the complexities of health services research, as well as outlining some recent data regarding complications of robotic vs. open radical prostatectomy. Finally, Professor Rob Pickard discussed the recent health technology assessment addressing the relative cost-effectiveness of robotic and laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Whilst the model requires a number of assumptions, it seems clear that centralisation of robotic surgery into high-volume centres is much more likely to result in acceptable cost-effectiveness, not to mention improved outcomes for patients.
In summary this has been a fantastic BAUS meeting for uro-oncological topics in particular and one I have thoroughly enjoyed attending. It seems the future uro-oncologist will need to be able to interpret and integrate advanced imaging techniques into their practice, make sophisticated decisions about when and how to defer treatment for prostate cancer, utilise a broad range of non-surgical treatments, and provide the very best surgical outcomes in a new era of transparency. I’m looking forward to the challenges ahead.
Ben Jackson
ST7 in Urological Surgery, Royal Derby Hospital
@Ben_L_jackson
Comments on this blog are now closed.
 This month’s topic for the Twitter-based International Urology Journal Club #urojc was bladder cancer, with a paper titled ‘Unaltered oncological outcomes of radical cystectomy with extended lymphadenectomy over three decades’ by Zehnder et al, published online in July 2013. Open access to the paper was kindly provided by the BJUI.
This month’s topic for the Twitter-based International Urology Journal Club #urojc was bladder cancer, with a paper titled ‘Unaltered oncological outcomes of radical cystectomy with extended lymphadenectomy over three decades’ by Zehnder et al, published online in July 2013. Open access to the paper was kindly provided by the BJUI.