Article of the month: Understanding volume–outcome relationships in nephrectomy and cystectomy for cancer: evidence from the UK Getting it Right First Time programme
Every month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and a video prepared by the authors; we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, we recommend this one.
Understanding volume–outcome relationships in nephrectomy and cystectomy for cancer: evidence from the UK Getting it Right First Time programme
William K. Gray*, Jamie Day*, Tim W. R. Briggs* and Simon Harrison*†
*Getting it Right First Time Programme, NHS England and NHS Improvement, London, UK and †Pinderfields Hospital, Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust, Wakefield, UK
Abstract
Objectives
To investigate volume–outcome relationships in nephrectomy and cystectomy for cancer.
Materials and Methods
Data were extracted from the UK Hospital Episodes Statistics database, which records data on all National Health Service (NHS) hospital admissions in England. Data were included for a 5‐year period (April 2013–March 2018 inclusive) and data on emergency and paediatric admissions were excluded. Data were extracted on the NHS trust and surgeon undertaking the procedure, the surgical technique used (open, laparoscopic or robot‐assisted) and length of hospital stay during the procedure. This dataset was supplemented by data on mortality from the UK Office for National Statistics. A number of volume thresholds and volume measures were investigated. Multilevel modelling was used to adjust for hierarchy and confounding factors.
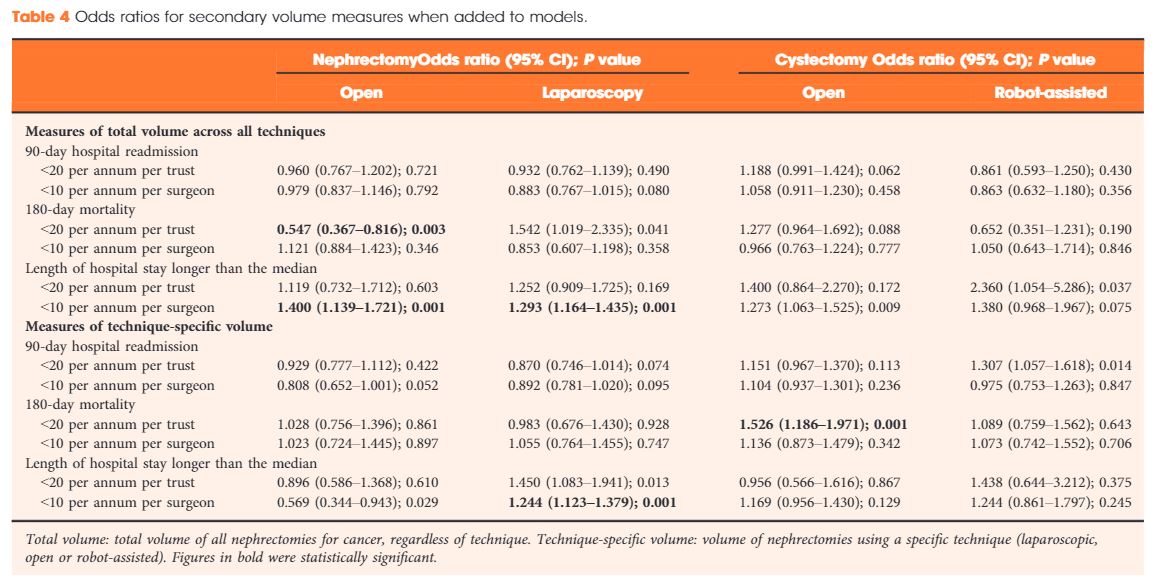 Results
Results
Data were available for 18 107 nephrectomy and 6762 cystectomy procedures for cancer. There was little evidence of trust or surgeon volume influencing readmission rates or mortality. There was some evidence of shorter length of hospital stay for high‐volume surgeons, although the volume measure and threshold used were important.
Conclusions
We found little evidence that further centralization of nephrectomy or cystectomy for cancer surgery will improve the patient outcomes investigated. It may be that length of stay can be optimized though training and support for lower‐volume centres, rather than further centralization.