Every month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and the authors have also kindly produced a video describing their work. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Cedric Lebacle* , Karim Bensalah†, Jean-Christophe Bernhard‡§, Laurence Albiges¶, Brigitte Laguerre**, Marine Gross-Goupil††, Herve Baumert‡‡, Herve Lang§§, Thibault Tricard§§, Brigitte Duclos¶¶, Armelle Arnoux***, Celine Piedvache***, Jean-Jacques Patard††† and Bernard Escudier¶
*Department of Urology, Bicêtre University Hospital, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, APHP, University Paris-Saclay, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, †Department of Urology, Pontchaillou University Hospital, Rennes, ‡Department of Urology, Bordeaux University Hospital, Pellegrin Hospital, §French Research Network on Kidney Cancer UroCCR, Bordeaux, ¶Department of Medicine, Gustave Roussy, University Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, **Department of Oncology, Eugene Marquis Centre, Rennes, ††Department of Medical Oncology, Bordeaux University Hospital, Saint-André Hospital, Bordeaux, ‡‡Department of Urology, Saint-Joseph Hospital, Paris, §§Department of Urology, Nouvel Hôpital Civil, ¶¶Department of Oncology, Hautepierre Hospital, Strasbourg University Hospital, Strasbourg, ***Paris-Sud Clinical Research Unit, Department of Statistics, Bicêtre University Hospital, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre and †††Department of Urology, Mont de Marsan Hospital, Mont de Marsan, France
Abstract
Objective
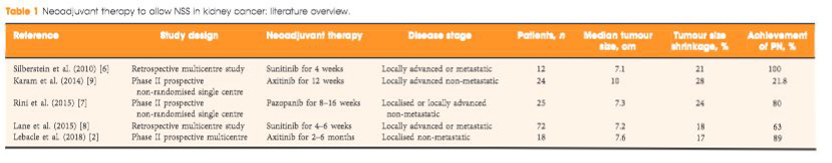
To evaluate the ability of neoadjuvant axitinib to reduce the size of T2 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) for shifting from a radical nephrectomy (RN) to a partial nephrectomy (PN) indication, offering preservation of renal function.
Patients and Methods
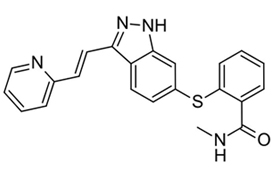
Patients with cT2aN0NxM0 clear‐cell RCC, considered not suitable for PN, were enrolled in a prospective, multicentre, phase II trial (AXIPAN). Axitinib 5 mg, and up to 7–10 mg, was administered twice daily, for 2–6 months before surgery, depending on the radiological response. The primary outcome was the number of patients receiving PN for a tumour <7 cm in size after neoadjuvant axitinib.
Results
Eighteen patients were enrolled. The median (range) tumour size and RENAL nephrometry score were 76.5 (70–98) mm and 11 (7–11), respectively. After axitinib neoadjuvant treatment, 16 tumours decreased in diameter, with a median size reduction of 17% (64.0 vs 76.5 mm; P < 0.001). The primary outcome was considered achieved in 12 patients who underwent PN for tumours <7 cm. Sixteen patients underwent PN. Axitinib was tolerated in the present study, as has been previously shown in the metastatic setting. Five patients had grade 3 adverse events. Five patients experienced Clavien III–V post‐surgery complications. At 2‐year follow‐up, six patients had metastatic progression, and two had a recurrence.
Conclusion
Neoadjuvant axitinib in cT2 ccRCC is feasible and, even with a modest decrease in size, allowed a tumour shrinkage <7 cm in 12 cases; however, PN procedures remained complex, requiring surgical expertise with possible morbidity.